Introduction
Hello, here is XueHaonan’s blog space.
About me
- Senior of Peking University majored in Computer Science.
- Active Participant of PKU lcpu-club.
- Enthusiastic about Rust programming.
Contact
- Github profile: https://github.com/xuehaonan27
- E-mail: xuehaonan27@gmail.com
Introduction
This section records develop process of COHPC (Cloud on HPC). The project has been made open source and source code could be found here.
Chapters
- Setup Slurm HPC cluster
- Build modules on HPC cluster
- Boot Windows on QEMU 9.2.0
- A bug caused by MAC address
CoHPC project introduction
This project is meant to build a system that could launch virtual machines on a HPC cluster.
On a HPC cluster, user could not have privilege (such as by sudo) and usually require user to submit tasks via task schedulers such as Slurm workload manager.
CoHPC provides a way to launch virtual machines and mount files into the virtual machine, and all these could be done without any privilege.
Possible application scenario
Assuming you processed a bunch of data on a HPC cluster. It’s usually big (especially data in fields like chemistry, biology, etc.) and expensive to download data and visualizing or processing them locally, while sometimes you might want to just have a look whether this bunch of data is feasible or not.
So with CoHPC you could launch a VM in seconds (including Windows ones), mount your data into the VM and utilize tools pre-installed in the VM to deal with the data, e.g. visualize them, and without transmitting all those data.
Setup Slurm HPC cluster
集群搭建目的
由于CoHPC项目计划部署在北大未名二号高性能计算平台上,在开发环节测试,首先自己部署一个Slurm集群。
集群搭建过程
集群规划与机器创建
本次部署计划部署一个master节点(由于仅需要一个测试环境,所以master同时作为管理节点、登录节点和数据传输节点)和四个compute节点。
我们有这些机器: 10.129.244.164 master01 10.129.244.75 compute01 10.129.240.45 compute02 10.129.243.221 compute03 10.129.240.20 compute04
机器初始化
在每一台RockyLinux机器上,sudo -i进入root,运行如下脚本来初始化机器环境。
sed -e 's|^mirrorlist=|#mirrorlist=|g' \
-e 's|^#baseurl=http://dl.rockylinux.org/$contentdir|baseurl=https://mirrors.pku.edu.cn/rocky|g' \
-i.bak \
/etc/yum.repos.d/rocky-extras.repo \
/etc/yum.repos.d/rocky.repo
dnf install -y 'dnf-command(config-manager)'
dnf install -y epel-release
dnf config-manager --set-enabled crb
sudo sed -e 's|^metalink=|#metalink=|g' \
-e 's|^#baseurl=https\?://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/|baseurl=https://mirrors.pku.edu.cn/epel/|g' \
-e 's|^#baseurl=https\?://download.example/pub/epel/|baseurl=https://mirrors.pku.edu.cn/epel/|g' \
-i.bak \
/etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo
dnf update -y
crb enable
dnf install -y vim bash-completion grubby
dnf group install -y "Headless Management" "System Tools" "Development Tools"
grubby --update-kernel ALL --args selinux=0
reboot
这段脚本将完成诸如基本依赖项安装、SELinux禁用等过程。
在各个机器上分别运行以下命令来确认主机名被更改:
hostnamectl set-hostname master01
hostnamectl set-hostname compute01
hostnamectl set-hostname compute02
hostnamectl set-hostname compute03
hostnamectl set-hostname compute04
在每一台机器上,vim /etc/hosts,添加以下内容来完成集群内机器IPv4地址和主机名的映射。
10.129.244.164 master01
10.129.244.75 compute01
10.129.240.45 compute02
10.129.243.221 compute03
10.129.240.20 compute04
机器时间同步
RockyLinux9.5采用chrony工具来完成时间同步,这对于启动Slurm集群重要(Slurm要求集群内机器时间同步)。
vim /etc/chrony.conf以编辑chrony配置。
在master01节点上,做如下修改(不是直接替换掉),配置其采用ntp.pku.edu.cn的授时服务。
# 禁用原有的授时服务
#pool 2.rocky.pool.ntp.org iburst
#sourcedir /run/chrony-dhcp
# 采用新的授时服务
server ntp.pku.edu.cn iburst
# 使得pku-new网络内其他机器可以采用本机器的NTP
allow 10.129.240.0/20
# Serve time
local stratum 10
在诸compute节点上,都做如下修改来采用master01的NTP服务。
# 禁用原有的授时服务
#pool 2.rocky.pool.ntp.org iburst
#sourcedir /run/chrony-dhcp
# 采用新的授时服务
server 10.129.244.164 iburst
在所有节点上都运行
systemctl restart chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd
来采用修改过的配置。
master01节点到其他节点免密登录
在master01节点上生成一个无pass phrase的密钥。
由于Clab上机器登录使用rocky用户,而我们进行配置时采用sudo -i切换到了root用户,该用户下.ssh应该还没有任何密钥对。直接键入ssh-keygen,然后一直按回车即可。
复制公钥:
cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub # 如果不是rsa,这个名字需要改变一下
在compute诸节点上,将该公钥添加进入/root/.ssh/authorized_keys。
然后应当可以从master01节点免密登录至诸计算节点。
ssh compute01
ssh compute02
ssh compute03
ssh compute04
NFS安装和配置
集群需要一个共享文件系统。采用NFS来配置。
服务端:master01
安装NFS、RPC服务
yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind
创建共享目录
mkdir /data
chmod 755 /data
键入vim /etc/exports并在文件中添加如下内容:
/data *(rw,sync,insecure,no_subtree_check,no_root_squash)
启动RPC和NFS服务
systemctl start rpcbind
systemctl start nfs-server
systemctl enable rpcbind
systemctl enable nfs-server
查看服务端是否正常加载配置文件
showmount -e localhost
# 有如下输出
Export list for localhost:
/data *
客户端:诸compute节点都运行
安装NFS客户端nfs-utils
yum install nfs-utils -y
查看服务端可共享的目录
# manage01 为NFS服务端IP
showmount -e master01
# 有如下输出
Export list for master01:
/data *
挂载服务端共享目录
# 创建目录
mkdir /data
#将来自manage01的共享存储/data 挂载至当前服务器的/data目录下
mount master01:/data /data -o proto=tcp -o nolock
设置开机自动挂载
键入vim /etc/fstab,在文档末尾添加
master01:/data /data nfs rw,auto,nofail,noatime,nolock,intr,tcp,actimeo=1800 0 0
查看挂载
df -h | grep data
# 有类似如下输出
master01:/data 79G 56M 75G 1% /data
测试挂载
# 例如在NFS服务端节点(其他节点也可以)写入一个测试文件
echo "hello nfs server" > /data/test.txt
cat /data/test.txt
# 在服务端节点或客户端节点均可以查看以下内容
hello nfs server
在共享文件系统中创建如下目录
# 创建home目录作为用户家目录的集合,可自定义
mkdir /data/home
# 创建software目录作为交互式应用的安装目录
mkdir /data/software
Munge安装
Munge是认证服务,实现本地或者远程主机进程的UID、GID验证。
需在每节点都有munge用户,且它们在各自节点上的UID和GID相同。
创建Munge用户
所有节点都创建Munge用户
groupadd -g 1108 munge
useradd -m -c "Munge Uid 'N' Gid Emporium" -d /var/lib/munge -u 1108 -g munge -s /sbin/nologin munge
生成熵池(entropy pool)
在master01节点上执行,安装rng工具,并采用/dev/urandom做熵源。
yum install -y rng-tools
rngd -r /dev/urandom
键入vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/rngd.service
修改如下
[service]
ExecStart=/sbin/rngd -f -r /dev/urandom
启动rngd
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl start rngd
systemctl enable rngd
# systemctl status rngd 查看服务状态
部署Munge
在所有节点上都执行
yum install epel-release -y
yum install munge munge-libs munge-devel -y
在master01节点上创建全局使用的密钥。
/usr/sbin/create-munge-key -r
dd if=/dev/urandom bs=1 count=1024 > /etc/munge/munge.key
将密钥同步到所有其他节点
scp -p /etc/munge/munge.key root@compute01:/etc/munge/
scp -p /etc/munge/munge.key root@compute02:/etc/munge/
scp -p /etc/munge/munge.key root@compute03:/etc/munge/
scp -p /etc/munge/munge.key root@compute04:/etc/munge/
# 在所有节点上赋权
chown munge: /etc/munge/munge.key
chmod 400 /etc/munge/munge.key
所有节点执行启动命令
systemctl start munge
systemctl enable munge
# systemctl status munge 查看服务状态
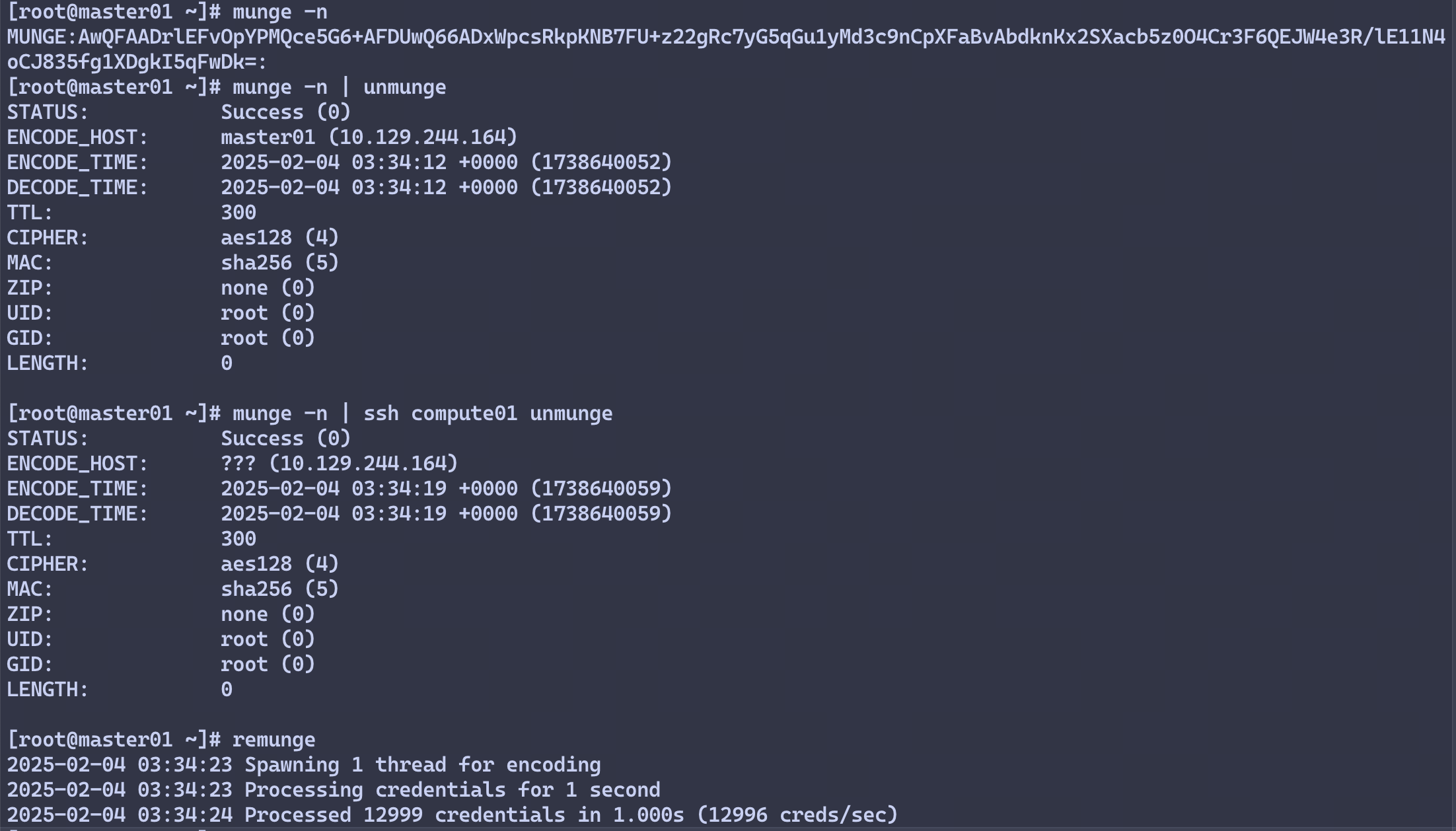
测试Munge服务
在master01节点执行
# 本地查看凭据
munge -n
# 本地解码
munge -n | unmunge
# 验证远程解码
munge -n | ssh compute01 unmunge
# munge凭证基准测试
remunge
示例输出
Slurm安装
安装mariadb
在master01节点安装mariadb,作为Slurm Accounting配置。 在master01执行
yum -y install mariadb-server
systemctl start mariadb
systemctl enable mariadb
ROOT_PASS=$(tr -dc A-Za-z0-9 </dev/urandom | head -c 16)
mysql -e "CREATE USER root IDENTIFIED BY '${ROOT_PASS}'"
mysql -uroot -p$ROOT_PASS -e 'create database slurm_acct_db'
创建slurm用户,并为其赋予slurm_acct_db数据库所有权。
mysql -uroot -p$ROOT_PASS
在数据库交互命令行中,键入
create user slurm;
grant all on slurm_acct_db.* TO 'slurm'@'localhost' identified by '123456' with grant option;
flush privileges;
exit
配置slurm
在所有节点执行
groupadd -g 1109 slurm
useradd -m -c "Slurm manager" -d /var/lib/slurm -u 1109 -g slurm -s /bin/bash slurm
安装slurm依赖
yum install gcc gcc-c++ readline-devel perl-ExtUtils-MakeMaker pam-devel rpm-build mysql-devel python3 -y
在master01节点制作RPM包 下载slurm
wget https://github.com/SchedMD/slurm/archive/refs/tags/slurm-24-11-1-1.tar.gz
安装rpmbuild,编译slurm,rpmbuild制作RPM包
yum install rpm-build -y
rpmbuild -ta --nodeps slurm-24.11.1.tar.bz2
制作完成后应在/root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64目录下得到.rpm包。
在诸compute节点运行
mkdir -p /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/
将master01编译好的RPM包拷贝到其他节点
scp -r /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64 root@compute01:/root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
scp -r /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64 root@compute02:/root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
scp -r /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64 root@compute03:/root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
scp -r /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64 root@compute04:/root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64
slurm安装与配置
在所有节点上都运行
cd /root/rpmbuild/RPMS/x86_64/
yum localinstall slurm-*
在master01节点上编辑slurm的配置文件。
cp /etc/slurm/cgroup.conf.example /etc/slurm/cgroup.conf
cp /etc/slurm/slurm.conf.example /etc/slurm/slurm.conf
cp /etc/slurm/slurmdbd.conf.example /etc/slurm/slurmdbd.conf
其中,slurm.conf和slurmdbd.conf可以参考文末附上的配置。
当然,推荐使用Slurm Configuration Tool来生成slurm.conf。
对于cgroup.conf,如果后续在compute节点上启动slurmd时遇到了cgroup/v2相关的错误,可以简单地在所有节点的/etc/slurm/cgroup.conf中添加这一行
CgroupPlugin=cgroup/v1
然后全部运行
mkdir -p /sys/fs/cgroup/freezer
mount -t cgroup -o freezer cgroup /sys/fs/cgroup/freezer
现在,复制配置文件到其他节点。
# slurmdbd.conf可不用复制,因为数据库运行在master01节点
scp -r /etc/slurm/*.conf root@compute01:/etc/slurm/
scp -r /etc/slurm/*.conf root@compute02:/etc/slurm/
scp -r /etc/slurm/*.conf root@compute03:/etc/slurm/
scp -r /etc/slurm/*.conf root@compute04:/etc/slurm/
在每一个节点上设置文件权限给slurm用户
mkdir /var/spool/slurmd
chown slurm: /var/spool/slurmd
mkdir /var/log/slurm
chown slurm: /var/log/slurm
mkdir /var/spool/slurmctld
chown slurm: /var/spool/slurmctld
启动服务
# 服务节点
systemctl start slurmdbd
systemctl enable slurmdbd
systemctl start slurmctld
systemctl enable slurmctld
# 所有节点
systemctl start slurmd
systemctl enable slurmd
# 通过 systemctl status ××× 查看服务状态,并确保个服务状态正常
可能的报错
# 1. 启动slurmdbd时报错(一):
slurmdbd: fatal: slurmdbd.conf file /etc/slurm/slurmdbd.conf should be 600 is 644 acc... others
# 解决方法
chmod 600 slurmdbd.conf
systemctl restart slurmdbd
# 2. 启动slurmdbd时报错(二):
slurmdbd: fatal: slurmdbd.conf not owned by SlurmUser root!=slurm
# 解决方法
chown slurm: /etc/slurm/slurmdbd.conf
systemctl restart slurmdbd
检查slurm集群
# 查看配置
scontrol show config
sinfo
scontrol show partition
scontrol show node
# 提交作业
srun -N2 hostname
scontrol show jobs
# 查看作业
squeue -a
配置QoS
# 查看已有的qos
sacctmgr show qos
# 创建low、high两个qos
sacctmgr create qos name=low
sacctmgr create qos name=high
# 给用户添加qos
sacctmgr modify user name={username} set qos=low,high,normal defaultQOS=low
Module安装
module给所有节点使用,因此放在NFS共享目录。在master01节点做这些事即可。
创建module安装目录
mkdir /data/software/module
TCL安装
module工具,依赖tcl工具,因此首先要安装tcl工具。
mkdir -p /data/software/module/tools/tcl
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/tcl/files/Tcl/9.0.1/tcl9.0.1-src.tar.gz
tar -zxvf tcl9.0.1-src.tar.gz
cd tcl9.0.1/unix/
# 注意改前缀
./configure --prefix=/data/software/module/tools/tcl
make
make install
Module安装
mkdir -p /data/software/module/tools/modules
wget https://sourceforge.net/projects/modules/files/Modules/modules-5.5.0/modules-5.5.0.tar.gz
tar -zxvf modules-5.5.0.tar.gz
cd modules-5.5.0/
./configure --prefix=/data/software/module/tools/modules \
--with-tclsh=/data/software/module/tools/tcl/bin/tclsh9.0 \
--with-tclinclude=/data/software/module/tools/tcl/include \
--with-tcl=/data/software/module/tools/tcl/lib/
make
make install
配置Module
安装完成后,在/data/software/module/tools/modules/目录下,就有module工具了。不过在/usr/bin/目录下,是没有module命令的。
配置环境变量
source /data/software/module/tools/modules/init/profile.sh
或者将该行加入~/.bashrc,以便在每次终端连接时初始化module环境。
参考文档
slurm.conf
# slurm.conf file generated by configurator.html.
# Put this file on all nodes of your cluster.
# See the slurm.conf man page for more information.
#
ClusterName=CoHPC
SlurmctldHost=master01
#SlurmctldHost=
#
#DisableRootJobs=NO
#EnforcePartLimits=NO
#Epilog=
#EpilogSlurmctld=
#FirstJobId=1
#MaxJobId=67043328
#GresTypes=
#GroupUpdateForce=0
#GroupUpdateTime=600
#JobFileAppend=0
#JobRequeue=1
#JobSubmitPlugins=lua
#KillOnBadExit=0
#LaunchType=launch/slurm
#Licenses=foo*4,bar
#MailProg=/bin/mail
#MaxJobCount=10000
#MaxStepCount=40000
#MaxTasksPerNode=512
#MpiDefault=
#MpiParams=ports=#-#
#PluginDir=
#PlugStackConfig=
#PrivateData=jobs
ProctrackType=proctrack/cgroup
#Prolog=
#PrologFlags=
#PrologSlurmctld=
#PropagatePrioProcess=0
#PropagateResourceLimits=
#PropagateResourceLimitsExcept=
#RebootProgram=
ReturnToService=1
SlurmctldPidFile=/var/run/slurmctld.pid
SlurmctldPort=6817
SlurmdPidFile=/var/run/slurmd.pid
SlurmdPort=6818
SlurmdSpoolDir=/var/spool/slurmd
SlurmUser=slurm
#SlurmdUser=root
#SrunEpilog=
#SrunProlog=
StateSaveLocation=/var/spool/slurmctld
#SwitchType=
#TaskEpilog=
TaskPlugin=task/affinity
#TaskProlog=
#TopologyPlugin=topology/tree
#TmpFS=/tmp
#TrackWCKey=no
#TreeWidth=
#UnkillableStepProgram=
#UsePAM=0
#
#
# TIMERS
#BatchStartTimeout=10
#CompleteWait=0
#EpilogMsgTime=2000
#GetEnvTimeout=2
#HealthCheckInterval=0
#HealthCheckProgram=
InactiveLimit=0
KillWait=30
#MessageTimeout=10
#ResvOverRun=0
MinJobAge=300
#OverTimeLimit=0
SlurmctldTimeout=120
SlurmdTimeout=300
#UnkillableStepTimeout=60
#VSizeFactor=0
Waittime=0
#
#
# SCHEDULING
#DefMemPerCPU=0
#MaxMemPerCPU=0
#SchedulerTimeSlice=30
SchedulerType=sched/backfill
SelectType=select/cons_tres
#
#
# JOB PRIORITY
#PriorityFlags=
#PriorityType=priority/multifactor
#PriorityDecayHalfLife=
#PriorityCalcPeriod=
#PriorityFavorSmall=
#PriorityMaxAge=
#PriorityUsageResetPeriod=
#PriorityWeightAge=
#PriorityWeightFairshare=
#PriorityWeightJobSize=
#PriorityWeightPartition=
#PriorityWeightQOS=
#
#
# LOGGING AND ACCOUNTING
AccountingStorageEnforce=associations,limits,qos
AccountingStorageHost=master01
AccountingStoragePass=/var/run/munge/munge.socket.2
AccountingStoragePort=6819
AccountingStorageType=accounting_storage/slurmdbd
#AccountingStorageUser=
#AccountingStoreFlags=
JobCompHost=localhost
JobCompLoc=slurm_acct_db
#JobCompParams=
JobCompPass=123456
JobCompPort=3306
JobCompType=jobcomp/mysql
JobCompUser=slurm
JobContainerType=job_container/none
JobAcctGatherFrequency=30
JobAcctGatherType=jobacct_gather/linux
SlurmctldDebug=info
SlurmctldLogFile=/var/log/slurmctld.log
SlurmdDebug=info
SlurmdLogFile=/var/log/slurmd.log
#SlurmSchedLogFile=
#SlurmSchedLogLevel=
#DebugFlags=
#
#
# POWER SAVE SUPPORT FOR IDLE NODES (optional)
#SuspendProgram=
#ResumeProgram=
#SuspendTimeout=
#ResumeTimeout=
#ResumeRate=
#SuspendExcNodes=
#SuspendExcParts=
#SuspendRate=
#SuspendTime=
#
#
# COMPUTE NODES
NodeName=master01 CPUs=2 State=UNKNOWN
NodeName=compute0[1-4] CPUs=4 State=UNKNOWN
PartitionName=compute Nodes=ALL Default=YES MaxTime=INFINITE State=UP
比较重要的是最后这部分,master01有2个CPU,compute诸节点各有4个CPU。Accounting和Job诸选项应当按照自己的需求配置。
slurmdbd.conf
#
# slurmdbd.conf file.
#
# See the slurmdbd.conf man page for more information.
#
# Authentication info
AuthType=auth/munge #认证方式,该处采用munge进行认证
AuthInfo=/var/run/munge/munge.socket.2 #为了与slurmctld控制节点通信的其它认证信息
#
# slurmDBD info
DbdAddr=localhost #数据库节点名
DbdHost=localhost #数据库IP地址
SlurmUser=slurm #用户数据库操作的用户
DebugLevel=verbose #调试信息级别,quiet:无调试信息;fatal:仅严重错误信息;error:仅错误信息; info:错误与通常信息;verbose:错误和详细信息;debug:错误、详细和调试信息;debug2:错误、详细和更多调试信息;debug3:错误、详细和甚至更多调试信息;debug4:错误、详细和甚至更多调试信息;debug5:错误、详细和甚至更多调试信息。debug数字越大,信息越详细
LogFile=/var/log/slurm/slurmdbd.log #slurmdbd守护进程日志文件绝对路径
PidFile=/var/run/slurmdbd.pid #slurmdbd守护进程存储进程号文件绝对路径
#
# Database info
StorageType=accounting_storage/mysql #数据存储类型
StoragePass=123456 #存储数据库密码
StorageUser=slurm #存储数据库用户名
StorageLoc=slurm_acct_db #数据库名称
Add packages to Module package manager
After installed Module package manager on HPC cluster, we should add packages.
Module environment
/data/software/src: for source code./data/software/modules/: for built binaries and libraries./data/software/module/tools/modules/modulefiles/: for packages’ Modulefile.
CMake
Pull from git repository or download via wget. Here I clone from git repository with version 3.31.5.
git clone git@github.com:Kitware/CMake.git --tag v3.31.5
cd v3.31.5/
mkdir /data/software/modules
./bootstrap --prefix=/data/software/modules/cmake/3.31.5
make -j $(nproc)
make install
Module file should be placed here: /data/software/module/tools/modules/modulefiles/cmake/3.25.0.
Modulefile content:
#%Module1.0
set version 3.31.5
set prefix /data/software/modules/cmake/$version
prepend-path PATH $prefix/bin
prepend-path MANPATH $prefix/share/man
prepend-path LD_LIBRARY_PATH $prefix/lib
Note:
PATHshould be the directory where the binaries exists ($prefix/binin this example).MANPATHshould be the directory where the manuals exists.LD_LIBRARY_PATHshould be the directory where the libraries exists for the loader and linker.
VDE-2
Pull source from sourceforge would not compile. I chose to clone source from Github.
git clone git@github.com:virtualsquare/vde-2.git
cd vde-2/
mkdir build
cd build/
cmake .. --install-prefix=/data/software/modules/vde/2.3.3
make -j$(nproc)
make install
Modulefile path: /data/software/module/tools/modules/modulefiles/vde/2.3.3.
Modulefile content:
#%Module1.0
set version 2.3.3
set prefix /data/software/modules/vde/$version
prepend-path PATH $prefix/bin
prepend-path LD_LIBRARY_PATH $prefix/lib
prepend-path MANPATH $prefix/share/man
QEMU
Pull source from QEMU official website.
wget https://download.qemu.org/qemu-9.2.0.tar.xz
tar -xvf qemu-9.2.0.tar.xz
cd qemu-9.2.0
Dependencies should be installed. Since my HPC cluster uses Rocky Linux, the package manager is dnf. But on other distributions, you should adopt different package managers and package name might be different as well.
dnf install python3-tomli
dnf install ninja
Compile QEMU with following command.
PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/data/software/modules/vde/2.3.3/lib64/pkgconfig:$PKG_CONFIG_PATH \
./configure \
--enable-kvm \
--enable-slirp \
--enable-vde \
--enable-system \
--enable-user \
--extra-cflags="-I/data/software/modules/vde/2.3.3/include/" \
--extra-ldflags="-L/data/software/modules/vde/2.3.3/lib64/" \
--prefix=/data/software/modules/qemu/9.2.0
Command explained:
- Note that I enabled some options in configuring phase because I need VDE and User network device support.
- On CentOS/RHEL,
PKG_CONFIG_PATHis required. --extra-cflagsis for C compiler.--extra-ldflagsis for linker.
Build and install.
make -j$(nproc)
make install
Boot Windows on QEMU 9.2.0
I tries to boot Windows on QEMU 9.2.0. This is how the process goes.
References
- This is the post that I take for reference.
- Get a
virtio-win.isodriver from here. - Get a Windows server ISO from here.
- VirtioFS reference from virtio-win.
Run the QEMU
I am doing this work on a HPC cluster with x86-64 architecture and a Linux operating system distribution.
I personally use Windows Server 2022 64bit En-US. Get with wget:
wget https://software-static.download.prss.microsoft.com/sg/download/888969d5-f34g-4e03-ac9d-1f9786c66749/SERVER_EVAL_x64FRE_en-us.iso
Get an empty and big enough disk in qcow2 format with qemu-img, here I name it as WindowsVM.img and give it 64G.
qemu-img create -f qcow2 WindowsVM.img 64G
Get UEFI bootloader.
Install the Windows operating system into the qcow2 disk.
# Replace this with your QEMU binary path
QEMU_BIN=/data/software/modules/qemu/9.2.0/bin/qemu-system-x86_64
# The VNC socket will be placed here
SOCK_PLACE=/data/home/testuser/.cohpc/vms/winuser/vnc.sock
# Path to the qcow2 disk
WIN_IMG=WindowsVM.img
# Path to the Windows ISO
WIN_ISO_PATH=SERVER_EVAL_x64FRE_en-us.iso
# Path to the virtio-win driver
VIRTIO_WIN_DRIVER=virtio-win.iso
# Path to UEFI bootloader OVMF code (read-only)
OVMF_CODE_PATH=/usr/share/edk2/ovmf/OVMF_CODE.fd
# Path to UEFI bootloader OVMF variables (read-write)
OVMF_VARS_PATH=./WindowsUEFIVM/OVMF_VARS.fd
${QEMU_BIN} \
-drive file=${WIN_IMG},format=qcow2,if=virtio \
-drive file=${WIN_ISO_PATH},media=cdrom \
-drive file=${VIRTIO_WIN_DRIVER},media=cdrom \
-boot order=d \
-enable-kvm \
-cpu host \
-m 6G \
-smp 4 \
-vnc unix:${SOCK_PLACE} \
-drive if=pflash,format=raw,file=${OVMF_CODE_PATH},readonly=on \
-drive if=pflash,format=raw,file=${OVMF_VARS_PATH}
Script explained:
- Because I run these scripts on a HPC cluster which adopts
modulesas package manager, so binary pathes might be strange. - I exposes a VNC socket to enable graphic user interface or it would be too difficult to manipulating with Windows.
- I am on x86-64 Linux so
-enable-kvmshould be enabled or the VM would be too slow. - We are booting from ISO so
-boot order=dis required. - It’s better copy a separate OVMF_VARS.fd for a new VM instance because it’s read-write.
Setup Windows
As said in this post mentioned above:
...
6. Continue with the installation procedure
7. Click "Custom: Install windows only"
8. Click Browse > CD Drive with the virtio-win drivers > amd64 > wXX (for windows 10 it would be w10 etc) and OK then Next
9. Continue
10. After the installation shut off the VM, and to run from the disk just remove the virtio drivers and the ISO from the command. Also if the network already is not working you can add
But since I am using Windows 11, so this is what I do:
- Click “Custom: Install windows only”
- Select
w11invirtio-windriver. - Then Windows could detect that 64G qcow2 disk, select it and install into it.
- Close the QEMU instance.
- Remove
virtio-win.isodrive and Windows ISO from the QEMU launch command and boot with qcow2 disk only.
This is the script:
# Replace this with your QEMU binary path.
QEMU_BIN=/data/software/modules/qemu/9.2.0/bin/qemu-system-x86_64
# The VNC socket will be placed here.
SOCK_PLACE=/data/home/testuser/.cohpc/vms/winuser/vnc.sock
# Path to the qcow2 disk
WIN_IMG=WindowsVM.img
# Path to UEFI bootloader OVMF code (read-only)
OVMF_CODE_PATH=/usr/share/edk2/ovmf/OVMF_CODE.fd
# Path to UEFI bootloader OVMF variables (read-write)
OVMF_VARS_PATH=./WindowsUEFIVM/OVMF_VARS.fd
${QEMU_BIN} \
-smp 4 \
-m 6G \
-cpu host \
-drive if=virtio,format=qcow2,file=${WIN_IMG} \
-enable-kvm \
-vnc ${SOCK_PLACE} \
-net nic \
-net user,hostname=windows \
-drive if=pflash,format=raw,file=${OVMF_CODE_PATH},readonly=on \
-drive if=pflash,format=raw,file=${OVMF_VARS_PATH}
Script explained:
-net user,hostname=windowsenables user network device, meaning we are using host network. Normal build of QEMU or QEMU installed by distribution package manager might not have user network enabled. Refer to this chapter for how to build a QEMU that fulfills requirement.
Now the Windows VM is launched, and could have access to host network. In my case, that means it could reach to the campus subnet and even Internet after log into the gateway.
Virtiofs: shared file system
To enable shared file system for mounting host files into the Windows VM, we should install virtiofs.
Reference could be found here.
To enable VirtioFS, we must add following lines into QEMU startup command and no line could be omitted. And virtio-win driver should also be added back.
...
-chardev socket,id=char0,path=/tmp/vhost-fs-1.sock \
-device vhost-user-fs-pci,queue-size=1024,chardev=char0,tag=my_virtiofs1 \
-chardev socket,id=char1,path=/tmp/vhost-fs-2.sock \
-device vhost-user-fs-pci,queue-size=1024,chardev=char1,tag=my_virtiofs2 \
-object memory-backend-memfd,id=mem,size=6G,share=on \
-numa node,memdev=mem \
Install WinFsp and VirtioFS
After logged into Windows VM, we could download WinFsp driver from this website: https://winfsp.dev (Remember that the VM could reach to host network now).
Personally I use this:
https://github.com/winfsp/winfsp/releases/download/v2.1B2/winfsp-2.1.24255.msi
After downloaded, run the installer and click next on and on.
Then install virtio drivers from virtio-win.iso disk mounted into the Windows VM. Click next on and on.
In Windows Device Manager, found Mass Storage Controller tab and Update Drive.
Mention that virtiofs could only have one instance by default, if we want to have multiple instances, virtiofs service must not be enabled and running, so stop and disable it in Windows Service.
And then we must setup WinFsp to replace virtiofs. In PowerShell:
"C:\Program Files (x86)\WinFsp\bin\fsreg.bat" virtiofs "<path to the binary>\virtiofs.exe" "-t %1 -m %2"
Install Windows on Aarch64 architecture
Reference could be found here.
Install from ISO into qcow2.
sudo qemu-system-aarch64 \
-device qemu-xhci -device usb-kbd -device usb-tablet \
-device usb-storage,drive=install \
-drive file=./Win11_24H2_English_Arm64.iso,media=cdrom,if=none,id=install \
-device usb-storage,drive=virtio-drivers \
-drive file=./virtio-win.iso.1,media=cdrom,if=none,id=virtio-drivers \
-drive file=./WindowsVMAarch64.qcow2,format=qcow2,if=virtio \
-device ramfb \
-boot order=d \
--accel kvm \
-machine virt \
-cpu host \
-m 8G \
-smp 8 \
-vnc 0.0.0.0:1 \
-bios /usr/share/qemu-efi-aarch64/QEMU_EFI.fd \
-nic user,model=virtio-net-pci
And rerun QEMU, but boot from qcow2 this time.
A Bug Caused by MAC Address
When developing CoHPC, I use QEMU to launch virtual machine and setup VM with cloud-init.
Add NIC in QEMU boot command:
${QEMU} \
-netdev vde,id=net0,sock=./vdesock \
-device e1000,netdev=net0,mac=${MAC_ADDRESS} \
-netdev user,id=user0,hostfwd=tcp::64306-:22 \
-device e1000,netdev=user0 \
...
I randomly generates MAC address into ${MAC_ADDRESS}.
In Network Config section in cloud-init, I adopted the same MAC address as in the QEMU command, and allocated a static IP address.
But QEMU log indicates that NIC might not be configured correctly randomly. It turns out that MAC address generation is wrong.
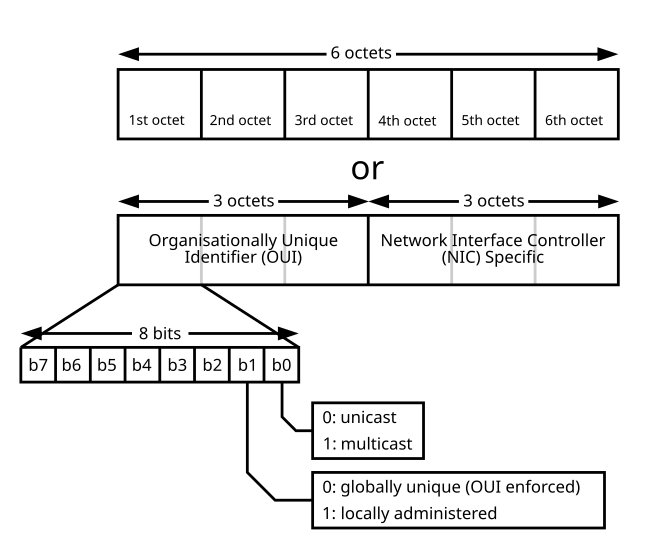
Since MAC address is randomly generated, so b0 bit in the first byte might be 1, meaning multicast and IP address could not be claimed by that NIC correctly. MAC should be unicast.
So the first 3 bytes of MAC address should not be randomly generated. Usually 52:00:00 is good. And the randomness could be left to latter 3 bytes.
Introduction
This section records some debuggings.
Fail to SSH log onto a MacOS server
Date: 2025-03-02 Error when SSH onto a MacOS error:
kex_exchange_identification: read: Connection reset by peer
Connection reset by <My IP Address...> port 22
Background
This server is connected via tailscale network and SSH login is enabled.
Solving
First try checking the log.
sudo log stream --predicate 'process == "sshd"' --info
Got these log information on my server:
Timestamp Thread Type Activity PID TTL
2025-03-02 23:07:56.155362+0800 0x15e23a Error 0x0 44960 0 sshd: (libsystem_info.dylib) [com.apple.network.libinfo:si_destination_compare] send failed: Invalid argument
2025-03-02 23:07:56.155878+0800 0x15e23a Error 0x0 44960 0 sshd: (libsystem_info.dylib) [com.apple.network.libinfo:si_destination_compare] send failed: Invalid argument
2025-03-02 23:07:56.155900+0800 0x15e23a Error 0x0 44960 0 sshd: (libsystem_info.dylib) [com.apple.network.libinfo:si_destination_compare] send failed: Invalid argument
2025-03-02 23:07:56.157492+0800 0x15e23a Info 0x0 44960 0 sshd: sshd: no hostkeys available -- exiting.
It turns out that tailscale is wrongly set. Allow Local Network Access should be enabled!
MySQL Connection Bug
On Ubuntu, install MySQL with apt install mysql-server, and root user could authenticate with auth_socket plugin and enable local cmdline login without password, but application could not access. Here’s the solving.
Step 1:modify MySQL root user auth method
- Login to MySQL (No password needed)
sudo mysql -u root - Check root user authentication method
If theSELECT user, plugin, host FROM mysql.user WHERE user = 'root';plugincolumn displaysauth_socket, you need to change it to password authentication. - Change the authentication method and set a password
ReplaceALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'yourpassword'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;yourpasswordwith a secure password - Exit MySQL
exit
Step 2:add password in Flask configuration
Modify the database configuration and add the password field:
DB_CONFIG = {
'host': 'localhost',
'user': 'root',
'password': 'yourpassword', # Add here
'database': 'TreeHole',
'charset': 'utf8mb4',
'cursorclass': DictCursor
}
Step 3: Ensure the database and permissions are correct
- Confirm that the database exists
After entering the password, check ifsudo mysql -u root -p -e "SHOW DATABASES;"TreeHoleexists (That’s my database). If not, create it:CREATE DATABASE TreeHole; - Grant permissions (usually root already has permissions, optional step)
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON TreeHole.* TO 'root'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Step 4: Restart the MySQL service
sudo systemctl restart mysql
Verify the connection
Test the connection via the command line using the configured password:
mysql -u root -p<yourpassword> -D TreeHole
If you successfully log in, the configuration is correct. The Flask application should be able to connect normally.
Other possible issues
- Database does not exist: Confirm that the
TreeHoledatabase has been created. - Firewall/SELinux restrictions: Local connections typically don’t have this issue, but you can check the relevant settings.
- PyMySQL version issue: Ensure you are using the latest version of
pymysql. Update with the command:
pip install --upgrade pymysql
Server Maintenance
Intranet Penetration by Tailscale and Clash
Background
I was home in holiday and sometimes need to log onto servers in campus net. However VPN tool suggested by university (Pulse Secure) is inconvenient.
Reference
My friend’s blog here.
Tailscale setup
On my personal computer (MacOS), tailscale could not run as a user space socks5 proxy server (Linux one could do so, though), so I want to run a tailscale user space proxy server on a Linux server in campus network, and route all traffic to campus network via clash to that Linux server.
On remote server (Linux):
echo 'net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf
echo 'net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 1' | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl -p
tailscale up --accept-routes --advertise-routes=<SUBNET_1>,<SUBNET_2>,...
Access tailscale dashboard (https://login.tailscale.com/admin/machines) and approve subnet routes.
Dante as socks5 server
<Local Machine TSIP> means Tailscale IP of my own personal computer. CIDR needed so /32 is good.
# /etc/danted.conf
logoutput: syslog stdout /var/log/sockd.log
internal: 0.0.0.0 port = 1055
external: tailscale0
socksmethod: username none #rfc931
clientmethod: none
#user.privileged: sockd
user.unprivileged: dante_user
client pass {
from: <本地机器TSIP地址> port 1-65535 to: 0.0.0.0/0
clientmethod: none
}
client block {
from: 0.0.0.0/0 to: 0.0.0.0/0
log: connect error
}
socks block {
from: 0.0.0.0/0 to: lo0
log: connect error
}
socks pass {
from: <本地机器TSIP地址> to: 0.0.0.0/0
protocol: tcp udp
}
And then:
sudo systemctl start danted
sudo systemctl enable danted
Clash redirect traffic to remote server
Start tailscale.
sudo tailscale up
tailscale ping <TS_IP>
Add Clash rules. The traffic to campus network will be redirected by Clash according to the rule, to the Tailscale virtual network interface into tailscale network.
Actually Clash Premium might have script modification functions, but I am too lazy to install another software, especially when that’s an opensource one and need build on my own. Write a Python script is not that boring though!
#! /usr/bin/env python3
import yaml
import sys
import os
TAILSCALE_ENTRY_MACHINE_TS_IP = ... # 入口Linux机器的Tailscale IP地址
TAILSCALE_ENTRY_MACHINE_ADVERTISED_SUBNET = ... # 入口Linux机器广播的IP子网
TAILSCALE_PROXY = {
"name": "Tailscale",
"type": "socks5",
"server": TAILSCALE_ENTRY_MACHINE_TS_IP,
"port": "1055",
"udp": True,
}
CAMPUS_RULES = [
["DOMAIN-SUFFIX", "pku.edu.cn", "CAMPUS"],
["DOMAIN-SUFFIX", "lcpu.dev", "CAMPUS"],
["IP-CIDR", TAILSCALE_ENTRY_MACHINE_ADVERTISED_SUBNET, "CAMPUS"]
]
def modify_clash_config(config_path: str):
# Backup original file
os.system(f"cp {config_path} {config_path}.bak")
# Load YAML config
with open(config_path, 'r') as f:
config = yaml.safe_load(f) or None
if not config:
print(f"Fail to load {config_path}")
return
# Insert proxy node
if 'proxies' not in config:
config['proxies'] = []
if not any(p['name'] == TAILSCALE_PROXY['name'] for p in config['proxies']):
config['proxies'].insert(0, TAILSCALE_PROXY)
# Insert proxy group
if 'proxy-groups' not in config:
config['proxy-groups'] = []
campus_group = next(
(g for g in config['proxy-groups'] if g['name'] == 'CAMPUS'),
None
)
if not campus_group:
campus_group = {
"name": "CAMPUS",
"type": "select",
"proxies": [TAILSCALE_PROXY['name'], "DIRECT"]
}
config['proxy-groups'].insert(0, campus_group)
else:
if TAILSCALE_PROXY['name'] not in campus_group['proxies']:
campus_group['proxies'].insert(0, TAILSCALE_PROXY['name'])
if 'rules' not in config:
config['rules'] = []
# Delete possible existing rules
config['rules'] = [r for r in config['rules']
if not (isinstance(r, str) and
(r.startswith("DOMAIN-SUFFIX,pku.edu.cn") or
r.startswith("DOMAIN-SUFFIX,lcpu.dev") or
r.startswith("IP-CIDR,"+TAILSCALE_ENTRY_MACHINE_ADVERTISED_SUBNET)))]
# Insert new rule
config['rules'] = [
f"{rule[0]},{rule[1]},{rule[2]}" for rule in CAMPUS_RULES] + config['rules']
with open(config_path, 'w') as f:
yaml.dump(config, f, allow_unicode=True, sort_keys=False)
print(f"Successfully modified {config_path}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print(f"Usage: {sys.argv[0]} <config.yaml>")
print(f"You probably want to use this:")
print()
print(f"python3 {sys.argv[0]} \"<path_to_this_script>\"")
sys.exit(1)
modify_clash_config(sys.argv[1])
Tips
Run this to get a hole!
sudo tailscale ping <LinuxMachineTSIP>
Deploy a Deepseek 8B model
Download
export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com
huggingface-cli download --resume-download deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B --local-dir DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B
export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com
huggingface-cli download --resume-download bartowski/Qwen_QwQ-32B-GGUF Qwen_QwQ-32B-Q8_0.gguf --local-dir Qwen_QwQ-32B-GGUF --local-dir-use-symlinks False
huggingface-cli download --resume-download bartowski/Qwen_QwQ-32B-GGUF Qwen_QwQ-32B-IQ2_XS.gguf --local-dir Qwen_QwQ-32B-GGUF --local-dir-use-symlinks False
Run server
MODEL_NAME=DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B
python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server --host=127.0.0.1 --port=8000 --model=$HOME/Projects/$MODEL_NAME --max_model_len=32768
Deploy a frontend with NextChat
I don’t want to use docker anymore, just deploy a NextChat front-end.
git clone git@github.com:ChatGPTNextWeb/NextChat.git
# Reference setup
# https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Yidadaa/ChatGPT-Next-Web/main/scripts/setup.sh
cd ChatGPT-Next-Web
yarn install
PORT=8081 yarn build
OPENAI_API_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8000/v1 \
OPENAI_API_KEY=EMPTY \
DEFAULT_MODEL=DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B \
PORT=8081 \
yarn start
# PORT=8081 yarn start
Build llama.cpp
cmake -B build \
-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=/usr/bin/clang \
-DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=/usr/bin/clang++ \
-DOpenMP_C_FLAGS="-Xpreprocessor -fopenmp -I$(brew --prefix libomp)/include" \
-DOpenMP_CXX_FLAGS="-Xpreprocessor -fopenmp -I$(brew --prefix libomp)/include" \
-DOpenMP_C_LIB_NAMES="omp" \
-DOpenMP_CXX_LIB_NAMES="omp" \
-DOpenMP_omp_LIBRARY=$(brew --prefix libomp)/lib/libomp.dylib
cmake --build build --config Release -j 8
Try LFS on MacMini M4
新买的MacMini M4到货了,可以开始配置。
Ref: https://www.linuxfromscratch.org/lfs/view/stable/
包管理策略
手动管理。Homebrew 用起来不太好用。
ClashXMeta
https://github.com/MetaCubeX/ClashX.Meta/releases/download/v1.4.9/ClashX.Meta.zip
拉取这个就行。我自己从源码构建失败了,应该是go版本的问题,懒得弄了。
Rust toolchain
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
在~/.cargo/config写入
[http]
proxy = "127.0.0.1:7890"
[https]
proxy = "127.0.0.1:7890"
Golang toolchain
https://go.dev/dl/go1.24.0.darwin-arm64.pkg
配置走国内镜像
go env -w GOPROXY=https://goproxy.cn
iTerm2
https://iterm2.com/downloads/stable/latest
之后配置iTerm2自己检查更新即可
Oh My Zsh
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ohmyzsh/ohmyzsh/master/tools/install.sh)"
没有代理用这个
sh -c "$(curl -fsSL https://install.ohmyz.sh/)"
Catppuccin Colors
git clone git@github.com:catppuccin/iterm
htop
curl -O https://github.com/htop-dev/htop/releases/download/3.3.0/htop-3.3.0.tar.xz
tar -xf htop-3.3.0.tar.xz
cd htop-3.3.0
./configure
make
sudo make install
nodejs with yarn
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.1/install.sh | bash
# in lieu of restarting the shell
. "$HOME/.nvm/nvm.sh"
# Download and install Node.js:
nvm install 22
# Verify the Node.js version:
node -v # Should print "v22.14.0".
nvm current # Should print "v22.14.0".
# Download and install Yarn:
corepack enable yarn
# Verify Yarn version:
yarn -v
GNU
首先使用 MacOS 自带的gcc(其实是clang)来编译一个gcc出来,然后我们继续使用这个gcc来编译其他GNU工具。 首先需要编译GCC依赖的库。
GMP
curl -O https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gmp/gmp-6.3.0.tar.xz
tar -xf gmp-6.3.0.tar.xz
cd gmp-6.3.0
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/gmp/6.3.0 \
--enable-cxx \
--enable-shared \
--enable-static
make
sudo make install
MPFR
curl -O https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/mpfr/mpfr-4.2.0.tar.xz
tar -xf mpfr-4.2.1.tar.xz
cd mpfr-4.2.1
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/mpfr/4.2.1 \
--with-gmp=/opt/gmp/6.3.0 \
--enable-shared \
--enable-static \
--enable-thread-safe \
--enable-formally-proven-code
make
sudo make install
MPC
curl -O curl -O https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/mpc/mpc-1.3.1.tar.gz
tar -xf mpc-1.3.1.tar.gz
cd mpc-1.3.1
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/mpc/1.3.1 \
--with-gmp=/opt/gmp/6.3.0 \
--with-mpfr=/opt/mpfr/4.2.1 \
--enable-shared \
--enable-static
make
sudo make install
ISL
curl -O https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/isl/isl-0.24.tar.xz
tar -xf isl-0.24.tar.xz
cd isl-0.24
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/isl/0.24 \
--enable-shared \
--enable-static \
--with-gmp-prefix=/opt/gmp/6.3.0
make
sudo make install
ZSTD
curl -O https://github.com/facebook/zstd/releases/download/v1.5.7/zstd-1.5.7.tar.gz
tar -xf zstd-1.5.7.tar.gz
cd zstd-1.5.7
make PREFIX=/opt/zstd/1.5.7
sudo make PREFIX=/opt/zstd/1.5.7 install
然后我们就可以构建一个尽可能完全的GCC了。
GCC
curl -O "https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/gcc-14.2.0/gcc-14.2.0.tar.gz"
curl -O "https://github.com/Homebrew/formula-patches/blob/master/gcc/gcc-14.2.0-r2.diff"
tar -xf gcc-14.2.0.tar.gz
cd gcc-14.2.0
patch -p1 < ../gcc-14.2.0-r2.diff
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/gcc/14.2.0 \
--disable-nls \
--enable-ld=yes \
--enable-gold=yes \
--enable-gprofng=yes \
--enable-year2038 \
--enable-libada \
--enable-libgm2 \
--enable-libssp \
--enable-bootstrap \
--enable-lto \
--enable-checking=release \
--with-gcc-major-version-only \
--enable-languages=c,c++,objc,obj-c++,fortran,m2 \
--with-gmp=/opt/gmp/6.3.0 \
--with-mpfr=/opt/mpfr/4.2.1 \
--with-mpc=/opt/mpc/1.3.1 \
--with-isl=/opt/isl/0.24 \
--with-zstd=/opt/zstd/1.5.7 \
--with-system-zlib \
--with-sysroot=/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX15.sdk \
--build=aarch64-apple-darwin24
make
sudo make install
binutils
curl -O "https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/binutils/binutils-with-gold-2.44.tar.gz"
tar -xf binutils-with-gold-2.44.tar.gz
cd binutils-with-gold-2.44
CC=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/gcc \
CXX=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/g++ \
AR=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/gcc-ar \
NM=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/gcc-nm \
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/binutils/2.44 \
--enable-gold=yes \
--enable-ld=yes \
--enable-year2038 \
--enable-libada \
--enable-libgm2 \
--enable-libssp \
--enable-pgo-build \
--enable-lto \
--with-zstd=/opt/zstd/1.5.7 \
--with-mpc=/opt/mpc/1.3.1 \
--with-mpfr=/opt/mpfr/4.2.1 \
--with-gmp=/opt/gmp/6.3.0 \
--with-isl=/opt/isl/0.24 \
--with-gcc-major-version-only \
--with-build-sysroot=/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX15.sdk \
--build=aarch64-apple-darwin24
# 然后自举
make clean
CC=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/gcc \
CPP=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/cpp \
CXX=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/g++ \
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/gcc/14.2.0 \
--disable-nls \
--enable-ld=yes \
--enable-gold=yes \
--enable-gprofng=yes \
--enable-year2038 \
--enable-libada \
--enable-libgm2 \
--enable-libssp \
--enable-bootstrap \
--enable-lto \
--enable-checking=release \
--with-gcc-major-version-only \
--enable-languages=c,c++,objc,obj-c++,fortran,m2 \
--with-gmp=/opt/gmp/6.3.0 \
--with-mpfr=/opt/mpfr/4.2.1 \
--with-mpc=/opt/mpc/1.3.1 \
--with-isl=/opt/isl/0.24 \
--with-zstd=/opt/zstd/1.5.7 \
--with-system-zlib \
--with-sysroot=/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX15.sdk \
--build=aarch64-apple-darwin24
make
sudo make install
Libraries have been installed in:
/opt/gcc/14.2.0/lib
If you ever happen to want to link against installed libraries
in a given directory, LIBDIR, you must either use libtool, and
specify the full pathname of the library, or use the `-LLIBDIR'
flag during linking and do at least one of the following:
- add LIBDIR to the `DYLD_LIBRARY_PATH' environment variable
during execution
See any operating system documentation about shared libraries for
more information, such as the ld(1) and ld.so(8) manual pages.
m4
curl -O "https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/m4/m4-1.4.19.tar.gz"
tar -xf m4-1.4.19.tar.gz
cd m4-1.4.19
CC=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/gcc \
CPP=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/cpp \
CXX=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/g++ \
./configure --prefix=/opt/m4/1.4.19
autoconf
curl -O "https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/autoconf/autoconf-2.72.tar.gz"
tar -xf autoconf-2.72.tar.gz
cd autoconf-2.72
./configure --prefix=/opt/autoconf/2.72 --with-gcc=/opt/gcc/14.2.0/bin/gcc
make
sudo make install
automake
autopoint
makeinfo
help2man
wget2
git clone https://github.com/wg/wget2.git
cd wget2
./bootstrap
./configure \
--prefix=/opt/wget2/2.0.0 \
--with-openssl \
--with-libpsl \
--with-libidn2 \
--with-libiconv \
Introduction
Things related with Managed Runtime research.
Debug OpenJDK 21 C2 compiler load barrier
Date: 2025-10-22
Background
For researching reason, load barrier should be added to OpenJDK 21 G1 GC heap, mimicking write reference field pre-barrier. But there’s bug.
Original code here
__ if_then(obj, BoolTest::ne, kit->null()); {
const int lru_sample_counter_offset = in_bytes(G1ThreadLocalData::lru_sample_counter_offset());
Node* lru_sample_counter_adr = __ AddP(no_base, tls, __ ConX(lru_sample_counter_offset));
Node* lru_sample_counter = __ load(__ ctrl(), lru_sample_counter_adr, TypeX_X, index_bt, Compile::AliasIdxRaw);
Node* next_counter = kit->gvn().transform(new SubXNode(lru_sample_counter, __ ConX(1)));
const TypeFunc* tf = load_ref_field_entry_Type();
__ make_leaf_call(tf, CAST_FROM_FN_PTR(address, G1BarrierSetRuntime::load_ref_field_entry), "load_ref_field_entry", obj, tls);
__ if_then(lru_sample_counter, BoolTest::ne, zeroX, unlikely); {
__ store(__ ctrl(), lru_sample_counter_adr, next_counter, index_bt, Compile::AliasIdxRaw, MemNode::unordered);
} __ else_(); {
}
__ end_if();
} __ end_if(); // (val != NULL)
Problem
G1BarrierSetRuntime::load_ref_field_entry isn’t actually called. If add log_info(gc)("..."); before and after the call, both of the logs could be printed normally but the call isn’t invoked actually.
Debugging
I doubt that the __ if_then(...); {...} __ else_(); {...} __ end_if(); block after the “leaf call” makes the call actually not a leaf call, so that’s might be the problem. So I modified the code piece into this:
__ if_then(obj, BoolTest::ne, kit->null()); {
const int lru_sample_counter_offset = in_bytes(G1ThreadLocalData::lru_sample_counter_offset());
Node* lru_sample_counter_adr = __ AddP(no_base, tls, __ ConX(lru_sample_counter_offset));
Node* lru_sample_counter = __ load(__ ctrl(), lru_sample_counter_adr, TypeX_X, index_bt, Compile::AliasIdxRaw);
Node* next_counter = kit->gvn().transform(new SubXNode(lru_sample_counter, __ ConX(1)));
__ if_then(lru_sample_counter, BoolTest::ne, zeroX, unlikely); {
__ store(__ ctrl(), lru_sample_counter_adr, next_counter, index_bt, Compile::AliasIdxRaw, MemNode::unordered);
} __ else_(); {
}
__ end_if();
const TypeFunc* tf = load_ref_field_entry_Type();
__ make_leaf_call(tf, CAST_FROM_FN_PTR(address, G1BarrierSetRuntime::load_ref_field_entry), "load_ref_field_entry", obj, tls);
// __ if_then(lru_sample_counter, BoolTest::ne, zeroX, unlikely); {
// __ store(__ ctrl(), lru_sample_counter_adr, next_counter, index_bt, Compile::AliasIdxRaw, MemNode::unordered);
// } __ else_(); {
// }
// __ end_if();
} __ end_if(); // (val != NULL)
Emm, notice that I just try to find out what’s the problem and I don’t care about the logic is right or not, so I just move the if then block to be in front of the call.
However this doesn’t compile!
Oh, I don’t mean compile error or something like that. It may compiles, but just takes way too much time that I don’t have much patience waiting it (for a bunch of hours). I doubt it’s because that load_ref_field_entry was filled with way too much logics (including nearly a hundred lines of code and serveral system calls, uh yes, system calls, in a load barrier!) that explodes when compiling. After I removed those logics, it compiles and, when running, triggered load_ref_field_entry finally.
So I tried several times and get this chart:
make_leaf_call before if | make_leaf_call after if | |
|---|---|---|
| Thin LB | Compiles fast, runs good | Compiles fast, runs good |
| Heavy LB | Compiles fast, runs with bug | Compiles extremely slow |
- With a thin load barrier,
load_ref_field_entryalways called. - With a heavy load barrier, if
make_leaf_callis placed beforeifblock, the code compiles butload_ref_field_entryis not invoked. - With a heavy load barrier and
make_leaf_callafterif, the code compiles extremely slow, and the compiled image explodes.
Analysis
I don’t know exactly how C2 compiler works so I can’t speak much, in case leading others into a wrong thinking way. But since whether make_leaf_call is placed before or after if doesn’t matters, it’s mysterious why when there’s a heavy load barrier, the code compiles and runs differently, one compiles fast but the leaf call seems to be removed, one compiles extremely slow and binary explodes.
OpenJDK 21 Hotspot JVM G1 GC explained
G1 GC 的算法原理不赘述,此处专门分析 OpenJDK 21 Hotspot JVM 的 G1 GC 具体实现细节。
重要的类
G1CollectedHeap
G1ConcurrentMark
G1YoungCollector
G1ParScanThreadState
各种 Closures
Hotspot JVM 采用大量的闭包来派发对每一个对象、堆区域或者线程要执行的动作。
-
Oop Closures:
-
Region Closures:
-
Thread Closures:
线程执行模型类
G1 GC 采用大量 GC Workers 并发地执行任务。每一个 Worker 都继承了 Thread 类,后者是 Hotspot JVM 中对操作系统提供的线程模型的平台无关抽象,在 Linux 操作系统下就对应一个 pthread。
-
Threads: Threads 是诸多 Thread 的集合,在 Hotspot JVM 中具有唯一实例(应该),并且兼具负责各个线程生命周期管理(创建、启动、停止、回收)以及 JVM 本身的启动工作。
-
Thread: Thread 是 Hotspot JVM 中对操作系统提供的线程模型的平台无关抽象。
-
WorkerThreads:
-
WorkerThread:
-
WorkTask:
-
WorkerTaskDispatcher:
标记过程
驱逐过程
Humongous 对象处理
OOP access logic in OpenJDK 21 Hotspot JVM
Cause there’s not much material telling me about how OOP access is implemented (apart from comments in OpenJDK Hotspot C++ code), I am going to analyze how OOP access implementation detail.
NOTE: implementation detail, not brief summary.
涉及到的文件列表如下
jdk21u/src/hotspot/share/oops/access.hpp
jdk21u/src/hotspot/share/oops/access.inline.hpp
jdk21u/src/hotspot/share/oops/accessBackend.hpp
jdk21u/src/hotspot/share/oops/accessBackend.inline.hpp
jdk21u/src/hotspot/share/oops/accessBackend.cpp
jdk21u/src/hotspot/share/oops/accessDecorators.hpp
OOP Access Operations
load: 从某一个地址加载值。
load_at: 给出基地址(base)和偏移量(offset)从这里加载一个值。
store: 存储一个值到某一地址。
store_at: 给出基地址(base)和偏移量(offset)向这里存储一个值。
atomic_cmpxchg: 对某一地址的值原子的 CAS 操作。
atomic_cpmxchg_at: 给出基地址(base)和偏移量(offset)对此处的值进行原子的 CAS 操作。
atomic_xchg: 对某一地址的值原子地进行交换。
atomic_xchg_at: 给出基地址(base)和偏移量(offset)对此处的值进行原子的交换。
OOP Access Decorators
对 OOP 的访问通过一系列 Decorators(装饰器)去附加语义。这里给它们做一个分类。
文件:src/hotspot/share/oops/accessDecorators.hpp
typedef uint64_t DecoratorSet;
template <DecoratorSet decorators, DecoratorSet decorator>
struct HasDecorator: public std::integral_constant<bool, (decorators & decorator) != 0> {};
DecoratorSet 为 64bit 宽的整数。HasDecorator 这个结构比较重要,它通过静态地将 decorator 与 decorators 做与运算来获取一个 bool 值来指导模板特化和 SFINAE 。
- General Decorators
DECORATORS_NONE: 全 0 值,表示空的装饰器集合,是默认值。
- Internal Decorators
INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP: 在启用了 UseCompressedOops 选项时,64 bit的 JVM 可以将 64 位宽度的 oop 指针压缩为 32 位宽度的 narrowOop 指针。当装饰器集合中有这个装饰器时,表示本次 oop access 需要在 oop 和 narrowOop 之间转换。INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP: 表示本次访问是 oop 访问,不是基本类型访问。
- Internal run-time Decorators
INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS: 当启用了 UseCompressedOops 选项时,该装饰器站在运行时解析的访问中会被设置(即需要 Runtime-dispatch 的访问)。
- Memory Ordering Decorators
MO_UNORDERED: 没有任何内存序保证,编译器和硬件可以以任何形式重排指令。MO_RELAXED: 表示原子的 load / store,编译器不重排该指令,但是硬件有可能重排。MO_ACQUIRE:MO_RELEASE:MO_SEQ_CST:
- Barrier Strength Decorators
AS_RAW: 该访问会被解释为裸的内存访问。忽略所有的语义(除了内存序和压缩oop指针)。绕过运行时函数指针分发(从预运行时分发就出去了,不再继续走流水线),所以也不会经过 GC 屏障。一般用在 JVM 内部对对象的访问中。- 对
oop*的访问会被解释为裸内存访问,不经过运行时检查。 - 对
narrowOop*的访问会被解释为 encoded / decoded 内存访问(涉及到指针变换),不经过运行时检查。 - 对
HeapWord*的访问会经过运行时检查,并且选择使用oop*访问或者narrowOop*访问。 - 对其他类型的访问会解释为裸内存访问,不经过运行时检查。
- 对
AS_NO_KEEPALIVE: 该次访问不会将目标对象保活。即在例如 ZGC 这种全并发 GC 算法中,Mutator 对对象的访问会通过 load barrier 将其标记为活对象(并且做指针自愈,指针染色转换等);或者通过 Reference 类型访问对象,这样的 access 就是保活的 (keepalive)。而加上了AS_NO_KEEPALIVE则表示该次访问不保活。但是访问会尊重例如 ZGC 中的并发驱逐、维护跨分代或者跨 Region 的指针。AS_NORMAL: 本次访问会被解析到一个BarrierSet类(具体是哪个子类取决于 GC 算法)的 accessor 上。注意对于基本类型的访问,只有合适的 build-time 装饰器被设置时,对基本类型的访问才会被解析到BarrierSet上,否则应该是一次裸内存访问。
- Reference Strength Decorators
ON_STRONG_OOP_REF: 访问 strongly reachable reference。ON_WEAK_OOP_REF: 访问 weakly reachable reference。ON_PHANTOM_OOP_REF: 访问 phantomly reachable reference。ON_UNKNOWN_OOP_REF: 不知道引用强度时。这个应用场景通常是在 unsafe API 中,从没有信息的地方传入一个不知道强度的引用。
- Access Location
IN_HEAP: 访问发生在 Java 堆内。如果IN_HEAP不设置的话,那么很多针对 Java 堆内对象的操作就不必要了,比如 G1 GC 维护卡表的行为。IN_NATIVE: 访问是在 Java 堆外的结构上发生的。基本就是本地堆了。IN_NMETHOD: 访问发生在一个 nmethod 上。
- Boolean Flag Decorators
IS_ARRAY: 访问发生在一个在 Java 堆上分配内存的 array 上。对于某些 GC 来说处理 oop 和处理 array 行为有所区别,对于这样的 GC,设置该装饰器就有必要。IS_DEST_UNINITIALIZED: 表示访问的值是未初始化的,比如对于 G1 GC 的 SATB 写屏障来说,被写掉的前值有可能根本就不是一个值,即那个引用就是个未初始化的状态,所以在写屏障拦截到这个写的时候,有可能就不用对前值做一些额外的操作和维护了(比如维护卡表和 Remember Set)。IS_NOT_NULL: 加速某些操作,比如 compress oop 的时候,如果能知道这个 oop 一定是非空的,那可以省下几个计算。
- Arraycopy Decorators
ARRAYCOPY_CHECKCAST: 复制时,如果能保证src array 的元素的类是 dst array 的元素的类的子类,那这种情况就比较好,就不需要设置ARRAYCOPY_CHECKCAST。但是如果不能保证,就要设置这个装饰器,在复制操作时插一个 check-cast barrier 进去做类型检查。ARRAYCOPY_DISJOINT: 表示 src array 和 dst array 能保证范围是不重合的。ARRAYCOPY_ARRAYOF: 该复制时 arrayof 形式的。ARRAYCOPY_ATOMIC: 访问需要是原子的 (over the size of its elements)。ARRAYCOOPY_ALIGNED: 访问需要与 HeapWord 对齐(8字节对齐)。
- Resolve barrier decorators
ACCESS_READ: 访问的目标对象是以 read-only 形式访问的。可以让 GC backend 使用更弱更高效的 barriers。ACCESS_WRITE: 访问的目标对象以 write 形式访问。
DECORATOR_LAST: 表示最后一个装饰器在哪里(最高bit在哪里)。
template<DecoratorSet input_decorators> struct DecoratorFixup: AllStatic 用于给 input_decorators 中没有设置装饰器的装饰器类别上配置默认值:
struct const DecoratorSet ref_strength_default: 如果 reference strength 类别中没设置,默认选择 strong。struct const DecoratorSet memory_ordering_default: 默认选择 unordered 内存序。struct const DecoratorSet barrier_strength_default: 默认选择 normal 的 barrier 强度。struct const DecoratorSet value = barrier_strength: 综合了以上三个默认值,是这个元函数的返回值,即默认装饰器集合。inline DecoratorSet decorator_fixup(DecoratorSet input_decorators, BasicType type)是不使用 metaprogramming 和 templates 的方式,即通过运行时函数调用做一样的事情。
OOP Access Steps
注意 Step 1 - 4 都是静态能够确定的,在编译器就静态派发好了;Step 5.a 存在因为 GC 类型等等信息必须是我们实际跑 JVM 时指定的,所以需要运行时参与;以及实际执行 GC 屏障也是运行时的。
Step 1
设置默认装饰器,将类型衰减 (Decay types),将 const 和 volatile 装饰符去掉。
Step 2
类型缩减 (Reduce types),因为在模板类型中,一个类型 T 和其指针类型 P 是两个 typename,T 和 P 的关系不明确,这一步的作用就是保证 P 是 T 的指针类型。
Step 3
预运行时分发(Pre-runtime dispatch)。检查 OOP 访问是否不需要运行时的调用(例如 GC barrier)。例如对于 Raw access 以及对基本类型(非对象)的访问(在 release build 中?),这类访问会直接在这里派发出来,不会继续沿流水线往下走。
Step 4
运行时分发(Runtime-dispatch),这一步主要是对 OOP 的访问,会委托给 GC 特定的访问屏障, 根据 BarrierSet::AccessBarrier 去添加一个 GC barrier。
Step 5.a
屏障解析。这一步应该是 Runtime-dispatch 首次发生时执行以下,起到一个初始化的作用。即对于 Step 4 运行时分发来说,顾名思义,在运行时才能获知具体要使用哪一个 GC,采用哪一个函数来派发,所以需要运行时一次初始化,在此之后就不需要了。
Step 5.b
后运行时派发 (Post-runtime dispatch)。
Basic definitions in access.hpp
该文件主要定义了:
template <DecoratorSet decorators = DECORATORS_NONE>
class Access: public AllStatic;
// Helper for performing raw accesses (knows only of memory ordering
// atomicity decorators as well as compressed oops).
template <DecoratorSet decorators = DECORATORS_NONE>
class RawAccess: public Access<AS_RAW | decorators> {};
// Helper for performing normal accesses on the heap. These accesses
// may resolve an accessor on a GC barrier set.
template <DecoratorSet decorators = DECORATORS_NONE>
class HeapAccess: public Access<IN_HEAP | decorators> {};
// Helper for performing normal accesses in roots. These accesses
// may resolve an accessor on a GC barrier set.
template <DecoratorSet decorators = DECORATORS_NONE>
class NativeAccess: public Access<IN_NATIVE | decorators> {};
// Helper for performing accesses in nmethods. These accesses
// may resolve an accessor on a GC barrier set.
template <DecoratorSet decorators = DECORATORS_NONE>
class NMethodAccess: public Access<IN_NMETHOD | decorators> {};
// Helper for array access.
template <DecoratorSet decorators = DECORATORS_NONE>
class ArrayAccess: public HeapAccess<IS_ARRAY | decorators>;
可以看到 access.hpp 中就是定义了一个 Class Access,其他的类都是 Access 预置了一个“访问来源”装饰器并作别名。所以接下来分析 Class Access 的具体实现。
verify_decorators
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
template <DecoratorSet expected_decorators>
void Access<decorators>::verify_decorators();
检查 Access 携带的装饰器是否合法。
- 不能有非法 bit。
- 某一类装饰器内部是互斥的,同一类中不可以同时设置多个。
阻止非法bit
该函数中 decorators 泛型参数是 Class Access 类型标签中的,代表该访问所携带的装饰器标签有哪些。 expected_decorators 涵盖了 Hotspot JVM 内置的所有装饰器标签。它的作用就是防止 decorators 中存在非法 bit,即实现的第一行:
STATIC_ASSERT((~expected_decorators & decorators) == 0); // unexpected decorator used
注意到使用了 STATIC_ASSERT 即是在编译器完成的。
屏障强度装饰器
const DecoratorSet barrier_strength_decorators = decorators & AS_DECORATOR_MASK;
STATIC_ASSERT(barrier_strength_decorators == 0 || ( // make sure barrier strength decorators are disjoint if set
(barrier_strength_decorators ^ AS_NO_KEEPALIVE) == 0 ||
(barrier_strength_decorators ^ AS_RAW) == 0 ||
(barrier_strength_decorators ^ AS_NORMAL) == 0
));
屏障强度装饰器有三类,AS_NO_KEEPALIVE,AS_RAW,AS_NORMAL。这个 STATIC_ASSERT 可以确保要么都不设置,要么只设置了其中一个。如果同时设置了多个,那么所有的异或操作都不会为0,该 STATIC_ASSERT 就会失效。
引用强度装饰器
const DecoratorSet ref_strength_decorators = decorators & ON_DECORATOR_MASK;
STATIC_ASSERT(ref_strength_decorators == 0 || ( // make sure ref strength decorators are disjoint if set
(ref_strength_decorators ^ ON_STRONG_OOP_REF) == 0 ||
(ref_strength_decorators ^ ON_WEAK_OOP_REF) == 0 ||
(ref_strength_decorators ^ ON_PHANTOM_OOP_REF) == 0 ||
(ref_strength_decorators ^ ON_UNKNOWN_OOP_REF) == 0
));
同理。引用强度是指 Java 语言中 java.lang.Reference 里面所定义的四种引用类型的不同强度。在这类只有强引用,弱引用,虚引用以及不知名的引用,并没有包括轻引用。也是只能有一个设置。
内存序装饰器
const DecoratorSet memory_ordering_decorators = decorators & MO_DECORATOR_MASK;
STATIC_ASSERT(memory_ordering_decorators == 0 || ( // make sure memory ordering decorators are disjoint if set
(memory_ordering_decorators ^ MO_UNORDERED) == 0 ||
(memory_ordering_decorators ^ MO_RELAXED) == 0 ||
(memory_ordering_decorators ^ MO_ACQUIRE) == 0 ||
(memory_ordering_decorators ^ MO_RELEASE) == 0 ||
(memory_ordering_decorators ^ MO_SEQ_CST) == 0
));
对于原子操作来说需要有内存序,该类装饰器确定了本次内存访问是否应该使用原子操作,如果是,那应该使用什么样子的内存序。
访问位置装饰器
const DecoratorSet location_decorators = decorators & IN_DECORATOR_MASK;
STATIC_ASSERT(location_decorators == 0 || ( // make sure location decorators are disjoint if set
(location_decorators ^ IN_NATIVE) == 0 ||
(location_decorators ^ IN_NMETHOD) == 0 ||
(location_decorators ^ IN_HEAP) == 0
));
这类装饰器确定了本次访问位于哪里。分三类,IN_NATIVE 表示访问在本地内存中;IN_NMETHOD 表示访问在 Java 方法中,因为 Java 方法中是存在一系列槽去放值的,部分值甚至对象会放在方法栈上(比较老的 JVM 则不会放对象在栈上);IN_HEAP 表示访问在 Java 堆中。
verify_primitive_decorators
template <DecoratorSet expected_mo_decorators>
static void verify_primitive_decorators() {
const DecoratorSet primitive_decorators = (AS_DECORATOR_MASK ^ AS_NO_KEEPALIVE) |
IN_HEAP | IS_ARRAY;
verify_decorators<expected_mo_decorators | primitive_decorators>();
}
在 AS_DECORATOR_MASK 去掉 AS_NO_KEEPALIVE,即 primitive_decorators 实际上为 AS_RAW | AS_NORMAL | IN_HEAP | IS_ARRAY。
verify_oop_decorators verify_heap_oop_decorators
template <DecoratorSet expected_mo_decorators>
static void verify_oop_decorators() {
const DecoratorSet oop_decorators = AS_DECORATOR_MASK | IN_DECORATOR_MASK |
(ON_DECORATOR_MASK ^ ON_UNKNOWN_OOP_REF) | // no unknown oop refs outside of the heap
IS_ARRAY | IS_NOT_NULL | IS_DEST_UNINITIALIZED;
verify_decorators<expected_mo_decorators | oop_decorators>();
}
template <DecoratorSet expected_mo_decorators>
static void verify_heap_oop_decorators() {
const DecoratorSet heap_oop_decorators = AS_DECORATOR_MASK | ON_DECORATOR_MASK |
IN_HEAP | IS_ARRAY | IS_NOT_NULL | IS_DEST_UNINITIALIZED;
verify_decorators<expected_mo_decorators | heap_oop_decorators>();
}
注意到 heap_oop_decorators 就是 oop_decorators 之外额外允许了 ON_UNKNOWN_OOP_REF,即堆中是可以用 unknown oop refs,而在 Java 堆外是不允许有这样的。
Special Decorator Set
static const DecoratorSet load_mo_decorators = MO_UNORDERED | MO_RELAXED | MO_ACQUIRE | MO_SEQ_CST;
static const DecoratorSet store_mo_decorators = MO_UNORDERED | MO_RELAXED | MO_RELEASE | MO_SEQ_CST;
static const DecoratorSet atomic_xchg_mo_decorators = MO_SEQ_CST;
static const DecoratorSet atomic_cmpxchg_mo_decorators = MO_RELAXED | MO_SEQ_CST;
额外预置了一些装饰集合。load 操作一般不需要 release,而 store 操作一般不需要 acquire。对于 atomic_xchg 一般必须是最强的 sequential consistent 的,而 atomic_cmpxchg 则额外允许了 relaxed 语义。这些都符合一般的原子操作的原则。
Basic definitions in accessBackend.hpp
该文件以及关联的 accessBackend.inline.hpp 以及 accessBackend.cpp 实现了 Step 1 - 4。
先回忆一下 accessDecorators.hpp 中定义的 HasDecorator。
template <DecoratorSet decorators, DecoratorSet decorator>
struct HasDecorator: public std::integral_constant<bool, (decorators & decorator) != 0> {};
它是一个元布尔值,传入 DecoratorSet decorators 和 DecoratorSet decorator,检查 decorator 是否在 decorators 中,并且将结果值存放在 value 中。
HeapOopType
// This metafunction returns either oop or narrowOop depending on whether
// an access needs to use compressed oops or not.
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
struct HeapOopType: AllStatic {
static const bool needs_oop_compress = HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP>::value &&
HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS>::value;
using type = std::conditional_t<needs_oop_compress, narrowOop, oop>;
};
这是一个 metafunction,传入 DecoratorSet decorators,检查 decorators 中是否设置了INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP 或者 INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS,静态地判断是否需要 oop compress,如果需要,那么对象指针应该是压缩过的 narrowOop,如果不需要那么应该是一般的 oop 类型,并且通过 std::conditional_t 将返回值结果放在 type 中。
BarrierType
enum BarrierType {
BARRIER_STORE,
BARRIER_STORE_AT,
BARRIER_LOAD,
BARRIER_LOAD_AT,
BARRIER_ATOMIC_CMPXCHG,
BARRIER_ATOMIC_CMPXCHG_AT,
BARRIER_ATOMIC_XCHG,
BARRIER_ATOMIC_XCHG_AT,
BARRIER_ARRAYCOPY,
BARRIER_CLONE
};
一个枚举,表示 barrier 是针对什么 oop operation 的。
MustConvertCompressedOop
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
struct MustConvertCompressedOop: public std::integral_constant<bool,
HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value &&
std::is_same<typename HeapOopType<decorators>::type, narrowOop>::value &&
std::is_same<T, oop>::value> {};
一个元布尔值,传入 DecoratorSet decorators 和 typename T,通过检查 decorators 中是否设置了 INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP、decorators 所指示的 HeapOopType(见上)是否为 narrowOop、以及 T 是否为 oop 这三者来确定自身的值是 true 还是 false。注意到只有当本次 access 配置的装饰器集合指示本次 access 是针对 narrowOop 的访问,并且 access 要求的返回值类型是 oop 是,才要求 must convert compress oop。
EncodedType
// This metafunction returns an appropriate oop type if the value is oop-like
// and otherwise returns the same type T.
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
struct EncodedType: AllStatic {
using type = std::conditional_t<HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value,
typename HeapOopType<decorators>::type,
T>;
};
这是一个元函数,传入参数 DecoratorSet decorators 和 typename T,检查本次 access 的装饰器集合中是否配置了 INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP,即本次访问是否是针对 oop 的访问?如果是的话那么就用 HeapOopType 从 decorators 中确定 oop 类型;如果不是的话那么就返回 T(即应该是一个基本类型访问)。
oop_field_addr
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
inline typename HeapOopType<decorators>::type*
oop_field_addr(oop base, ptrdiff_t byte_offset) {
return reinterpret_cast<typename HeapOopType<decorators>::type*>(
reinterpret_cast<intptr_t>((void*)base) + byte_offset);
}
一个一般的 Cpp 函数,返回值类型通过 HeapOopType 从元参数 DecoratorSet decorators 中提取,作用应该是给那些带有 _at 后缀的 OOP operation 组合出实际上应当访问的地址。一个简单的指针偏移,没啥好说的。
PossiblyLockedAccess
// This metafunction returns whether it is possible for a type T to require
// locking to support wide atomics or not.
template <typename T>
#ifdef SUPPORTS_NATIVE_CX8
struct PossiblyLockedAccess: public std::false_type {};
#else
struct PossiblyLockedAccess: public std::integral_constant<bool, (sizeof(T) > 4)> {};
#endif
一个元函数,对于位宽较大的类型,可能硬件不支持单指令原子操作,需要加 lock 然后进行宽原子操作。
Access Pipeline
这一部分具体介绍 Access 的流水线式派发。
OOP type canonicalization
template <typename T>
struct OopOrNarrowOopInternal: AllStatic {
typedef oop type;
};
template <>
struct OopOrNarrowOopInternal<narrowOop>: AllStatic {
typedef narrowOop type;
};
// This metafunction returns a canonicalized oop/narrowOop type for a passed
// in oop-like types passed in from oop_* overloads where the user has sworn
// that the passed in values should be oop-like (e.g. oop, oopDesc*, arrayOop,
// narrowOoop, instanceOopDesc*, and random other things).
// In the oop_* overloads, it must hold that if the passed in type T is not
// narrowOop, then it by contract has to be one of many oop-like types implicitly
// convertible to oop, and hence returns oop as the canonical oop type.
// If it turns out it was not, then the implicit conversion to oop will fail
// to compile, as desired.
template <typename T>
struct OopOrNarrowOop: AllStatic {
typedef typename OopOrNarrowOopInternal<std::decay_t<T>>::type type;
};
OopOrNarrowOop 做了类型规范化。
- 如果传入的
T类型是narrowOop,那没什么好说还是narrowOop(直接匹配OopOrNarrowOopInternal<narrowOop>)。 - 如果传入的
T类型是oop或者可以隐式转换为oop的类型(例如oopDesc*,arrayOop,instanceOopDesc*)则会规范化到oop(匹配OopOrNarrowOopInternal<narrowOop>失败,去匹配更弱一级的template <typename T> OopOrNarrowOopInternal,就会都变成oop类型)。 - 如果传入的
T对上述两个都匹配失败,那么说明根本不是一个对象指针传进来了,应该 Error,编译失败,符合预期。
Step 1
完成如下几件事情:
- 类型检查。
- 类型衰减(decay type),去除 const 和 volatile 关键字。
- 补全装饰器,对未设置装饰器值的类别补上一个默认值(上文已述)。如果是 volatile 的那么默认内存序不是 unordered 而是 relaxed。
这一步仍然是用 load 操作来举例子。
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename P, typename T>
inline T load(P* addr) {
verify_types<decorators, T>();
using DecayedP = std::decay_t<P>;
using DecayedT = std::conditional_t<HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value,
typename OopOrNarrowOop<T>::type,
std::decay_t<T>>;
// If a volatile address is passed in but no memory ordering decorator,
// set the memory ordering to MO_RELAXED by default.
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = DecoratorFixup<
(std::is_volatile<P>::value && !HasDecorator<decorators, MO_DECORATOR_MASK>::value) ?
(MO_RELAXED | decorators) : decorators>::value;
return load_reduce_types<expanded_decorators, DecayedT>(const_cast<DecayedP*>(addr));
}
Verify types
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
static void verify_types(){
// If this fails to compile, then you have sent in something that is
// not recognized as a valid primitive type to a primitive Access function.
STATIC_ASSERT((HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value || // oops have already been validated
(std::is_pointer<T>::value || std::is_integral<T>::value) ||
std::is_floating_point<T>::value)); // not allowed primitive type
}
所有流水线派发的第一步都会调用这个 verify_types。它会静态检查类型:
- 是 OOP
- 是 pointer
- 是 integral
- 是 floating point 除此之外的类型都不允许。
Decay type
using DecayedP = std::decay_t<P>;
using DecayedT = std::conditional_t<HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value,
typename OopOrNarrowOop<T>::type,
std::decay_t<T>>;
在上面 load 的代码中可以看到,这里静态地利用了 std::decay_t 做了类型衰减,将指针 P 类型衰减为 DecayedP,将返回值类型 T 衰减为 DecayedT。其中 T 会进行一次特判,即如果是 OOP 类型的话,会利用前文所述的 OopOrNarrowOop 规范化为 oop 或者 narrowOop;如果是基本类型,那么就是用 std::decay_t 去除 CV 限定符(其实 std::decay_t 所做的不仅仅是这些,它会综合处理所有按值传递相关的转换,但是由于之前已经经过了类型检查,所以针对通过检查的类型基本能做的就是 CV 限定符去除了)。
Decorators fixup
这一步补全装饰器集合。
// If a volatile address is passed in but no memory ordering decorator,
// set the memory ordering to MO_RELAXED by default.
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = DecoratorFixup<
(std::is_volatile<P>::value && !HasDecorator<decorators, MO_DECORATOR_MASK>::value) ?
(MO_RELAXED | decorators) : decorators>::value;
DecoratorFixup 之前已经介绍过,它作为一个元函数,会将传入的装饰器集合补全(将没设置的类别补上一个默认值),并用 value 返回出来。那么现在看一下传入的装饰器集合:
(std::is_volatile<P>::value && !HasDecorator<decorators, MO_DECORATOR_MASK>::value) ?
(MO_RELAXED | decorators) : decorators
- 如果目前内存序类别中已经有装饰器了,那么就直接原样传入即可。
- 如果内存序类别中没有装饰器而且指针类型 P 是带着 volatile 关键字的,那么设置一个
MO_RELAXED进去,这样DecoratorFixup就只会修复别的类别了。 - 如果内存序类别中没有配置装饰器而且指针类型 P 不是 volatile 的,那么还是原样传入,让
DecoratorFixup加上默认的MO_UNORDERED。
Invoke implementation
在类型检查和规范化都完成之后,就进入了流水线的下一步。
return load_reduce_types<expanded_decorators, DecayedT>(const_cast<DecayedP*>(addr));
带着修复好的装饰器集合以及通过类型检查、类型衰减和规范化的 DecayedT 和 DecayedP,进入 Step 2。
Step 2: Reduce types
这一步检查 P 和 T 的类型,保证 P 和 T 是匹配的,即 P 是对应类型的指针类型,而 T 是对应类型的值类型。将错误的类型利用 SFINAE 报编译错误,并且将基本类型和 OOP 类型利用 SFINAE 分流,分开匹配。可以看一下这部分的注释。
` // Step 2: Reduce types.
// Enforce that for non-oop types, T and P have to be strictly the same.
// P is the type of the address and T is the type of the values.
// As for oop types, it is allow to send T in {narrowOop, oop} and
// P in {narrowOop, oop, HeapWord*}. The following rules apply according to
// the subsequent table. (columns are P, rows are T)
// | | HeapWord | oop | narrowOop |
// | oop | rt-comp | hw-none | hw-comp |
// | narrowOop | x | x | hw-none |
//
// x means not allowed
// rt-comp means it must be checked at runtime whether the oop is compressed.
// hw-none means it is statically known the oop will not be compressed.
// hw-comp means it is statically known the oop will be compressed.
注意到 P = pointer to HeapWord* T = oop 的情况下需要运行时检查 P 这个地方存的是什么,如果是 oop 还好直接返回;如果是 narrowOop 就需要一步转换。而 P = pointer to oop T = narrowOop 是不允许的,这样会用位宽大的指针加载位宽小的值;同理 P = pointer to HeapWord* T = narrowOop 也不允许,因为 P 指的地方有可能真是一个 oop,这样也有可能位宽大的指针加载位宽小的值。
还是以 load 举例。
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
inline T load_reduce_types(T* addr) {
return PreRuntimeDispatch::load<decorators, T>(addr);
}
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
inline typename OopOrNarrowOop<T>::type load_reduce_types(narrowOop* addr) {
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = decorators | INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP |
INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS;
return PreRuntimeDispatch::load<expanded_decorators, typename OopOrNarrowOop<T>::type>(addr);
}
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
inline oop load_reduce_types(HeapWord* addr) {
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = decorators | INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP;
return PreRuntimeDispatch::load<expanded_decorators, oop>(addr);
}
三个 load_reduce_types,分别匹配:
- 第一个,指针和值类型一样,匹配
narrowOop* narrowOop和oop* oop的情况。不需要增加任何的装饰器。 - 第二个,指针是
narrowOop*的,那么值就有可能是narrowOop或者oop的,通过OopOrNarrowOop根据装饰器集合判断。并且添加INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP和INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS两个装饰器,需要进行一下解压缩。 - 第三个,指针是
HeapWord*的,那么值就只能是oop。添加INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP这个装饰器。
在经过 Step 2 的 Reduce types 之后,会进入 Step 3 的预运行时分发。
Step 3: Pre-runtime dispatch
预运行时分发阶段根据 barrier strength decorators,过滤掉 Raw Access,将它们直接生成代码,而不再继续向下走流水线,并且让 RawAccessBarrier 处理压缩指针和内存序装饰器;对于其他类型的访问,则继续经过运行时检查。
struct PreRuntimeDispatch: AllStatic {
template<DecoratorSet decorators>
struct CanHardwireRaw: public std::integral_constant<
bool,
!HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value || // primitive access
!HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP>::value || // don't care about compressed oops (oop* address)
HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS>::value> // we can infer we use compressed oops (narrowOop* address)
{};
static const DecoratorSet convert_compressed_oops = INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS | INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP;
template<DecoratorSet decorators>
static bool is_hardwired_primitive() {
return !HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value;
}
首先 CanHardwireRaw 是一个元布尔值,为 true 时:
- 装饰器表明这是一个基本类型访问。
- 该访问是 OOP 访问,但是不需要关心 OOP 指针压缩问题。
- 该访问是 OOP 访问,而且需要 Runtime 进行指针压缩解压缩操作。
如果 CanHardwireRaw 是真值,
还是以 load 操作举例。
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
inline static typename EnableIf<
HasDecorator<decorators, AS_RAW>::value && CanHardwireRaw<decorators>::value, T>::type
load(void* addr) {
typedef RawAccessBarrier<decorators & RAW_DECORATOR_MASK> Raw;
if (HasDecorator<decorators, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value) {
return Raw::template oop_load<T>(addr);
} else {
return Raw::template load<T>(addr);
}
}
匹配到这个 load 的,说明:
- 本次 Access 是
AS_RAW的。 - 本次 Access 可以直接转化为硬编码。
那么再根据是 OOP 访问还是基本类型访问,调用 RawAccessBarrier 中的 oop_load 或者 load 即可,RawAccessBarrier 会继续处理,直接生成 C++ 代码,并由编译器编为二进制。
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
inline static typename EnableIf<
HasDecorator<decorators, AS_RAW>::value && !CanHardwireRaw<decorators>::value, T>::type
load(void* addr) {
if (UseCompressedOops) {
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = decorators | convert_compressed_oops;
return PreRuntimeDispatch::load<expanded_decorators, T>(addr);
} else {
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = decorators & ~convert_compressed_oops;
return PreRuntimeDispatch::load<expanded_decorators, T>(addr);
}
}
而对于无法直接特化为 C++ 代码的 Raw access,应该是在 CanHardwireRaw 中出了问题,这里会根据 OOP 访问还是基本类型访问,补全或者去除掉 INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS 和 INTERNAL_CONVERT_COMPRESSED_OOP; 这两个装饰器,然后再一次尝试匹配,这次匹配到第一个 load。
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
inline static typename EnableIf<
!HasDecorator<decorators, AS_RAW>::value, T>::type
load(void* addr) {
if (is_hardwired_primitive<decorators>()) {
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = decorators | AS_RAW;
return PreRuntimeDispatch::load<expanded_decorators, T>(addr);
} else {
return RuntimeDispatch<decorators, T, BARRIER_LOAD>::load(addr);
}
}
而对于不是 Raw Access 的访问来说,会匹配到这个 load 上来。
- 对于基本类型的访问来说,即使是
AS_NORMAL或别的什么访问类型,也可以被当做 Raw Access 直接生成 C++ 代码了,因为没啥区别,所以加上AS_RAW装饰器并再次匹配,这次匹配就应该匹配到第一个 load 并直接特化为 C++ 代码了。 - 对于非 Raw Access 的 OOP access 来说,就无法在静态确定如何生成 C++ 代码了,就需要进入 Runtime,并且根据 OOP operation 类型附加上一个 barrier 类型,比如 load 就是
BARRIER_LOAD。
RawAccessBarrier
这个类比较大,主要是执行 Raw Access 用的,里面的方法用于 Raw Access 派发。
// The RawAccessBarrier performs raw accesses with additional knowledge of
// memory ordering, so that OrderAccess/Atomic is called when necessary.
// It additionally handles compressed oops, and hence is not completely "raw"
// strictly speaking.
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
class RawAccessBarrier: public AllStatic;
注意到注释提到,RawAccessBarrier 虽然声称是执行 RawAccess 的,但是其实还会考虑到内存序、oop压缩指针等。
// This mask specifies what decorators are relevant for raw accesses. When passing
// accesses to the raw layer, irrelevant decorators are removed.
const DecoratorSet RAW_DECORATOR_MASK = INTERNAL_DECORATOR_MASK | MO_DECORATOR_MASK |
ARRAYCOPY_DECORATOR_MASK | IS_NOT_NULL;
定义了 RawAccessBarrier 所关心的所有装饰器类型。
field_addr
static inline void* field_addr(oop base, ptrdiff_t byte_offset) {
return AccessInternal::field_addr(base, byte_offset);
}
代理一下之前见到的 field_addr 简单的计算一下地址。
encode / decode
// Only encode if INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP
template <DecoratorSet idecorators, typename T>
static inline typename EnableIf<
AccessInternal::MustConvertCompressedOop<idecorators, T>::value,
typename HeapOopType<idecorators>::type>::type
encode_internal(T value);
template <DecoratorSet idecorators, typename T>
static inline typename EnableIf<
!AccessInternal::MustConvertCompressedOop<idecorators, T>::value, T>::type
encode_internal(T value) {
return value;
}
template <typename T>
static inline typename AccessInternal::EncodedType<decorators, T>::type
encode(T value) {
return encode_internal<decorators, T>(value);
}
// Only decode if INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP
template <DecoratorSet idecorators, typename T>
static inline typename EnableIf<
AccessInternal::MustConvertCompressedOop<idecorators, T>::value, T>::type
decode_internal(typename HeapOopType<idecorators>::type value);
template <DecoratorSet idecorators, typename T>
static inline typename EnableIf<
!AccessInternal::MustConvertCompressedOop<idecorators, T>::value, T>::type
decode_internal(T value) {
return value;
}
template <typename T>
static inline T decode(typename AccessInternal::EncodedType<decorators, T>::type value) {
return decode_internal<decorators, T>(value);
}
注意到这些函数定义中使用的元参数 DecoratorSet idecorators 和 RawAccessBarrier 类型定义中的元参数 DecoratorSet decorators 是不一样的,即类成员函数的模板不绑定到类模板上。
注意这里面使用了 SFINAE (Substitution Failure Is Not An Error),其中 EnableIf 就是 std::enable_if 的别名。会利用前文所述的元布尔值 MustConvertCompressedOop 检查传入的 idecorators 是否需要进行 Oop 压缩指针转换到 T,并且指针转换目标类型由 HeapOopType 元函数计算得出,即第一个 encode_internal 会执行压缩指针相关的。而这个 encode_internal 的实现细节如下:
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
template <DecoratorSet idecorators, typename T>
inline typename EnableIf<
AccessInternal::MustConvertCompressedOop<idecorators, T>::value,
typename HeapOopType<idecorators>::type>::type
RawAccessBarrier<decorators>::encode_internal(T value) {
if (HasDecorator<decorators, IS_NOT_NULL>::value) {
return CompressedOops::encode_not_null(value);
} else {
return CompressedOops::encode(value);
}
}
注意到之前提到的 IS_NOT_NULL 装饰器在这里就发挥了作用:如果能够保证这个访问的 OOP 指针不是空指针,那么就可以调用开销较小的 encode_not_null 上了(少一次if,即 cmov 应该是)。
而如果第一个 encode_internal 匹配失败,它就是 Failure 而不是 Error,会继续尝试匹配第二个 encode_internal,即如果 MustConvertCompressedOop 检查到 idecorators 指示的 OOP 类型到 T 不需要压缩指针转换,那么就会匹配到这个 encode_internal 上,由于 idecorators 指示的返回类型应该是和 T 一致的,所以直接原样返回即可,不需要额外的编码逻辑。
而下方的 encode 函数则是对上方所有的 encode_internal 进行了封装,并且元参数和 RawAccessBarrier 保持一致了。这样,对基本类型、oop 类型和 narrowOop 类型的访问就统一使用了 encode 一个函数即可。
下方 decode 同样逻辑。总结 encode / decode 封装了 RawAccessBarrier 对 OOP 指针压缩的操作,通过 SFINAE 在编译期静态派发到具体函数。
load / store / atomic_cmpxchg / atomic_xchg
和上文所述的 encode / decode 一样,如果说它们利用 SFINAE 实现并封装了 RawAccessBarrier 关于 OOP 指针压缩的操作,那么这部分就是利用 SFINAE 实现并封装了 RawAccessBarrier 关于原子和内存序的操作。
以 load 操作举例分析,其他操作逻辑一样。
template <typename T>
static inline T load(void* addr) {
return load_internal<decorators, T>(addr);
}
template <DecoratorSet ds, typename T>
static typename EnableIf<
HasDecorator<ds, MO_SEQ_CST>::value, T>::type
load_internal(void* addr);
template <DecoratorSet ds, typename T>
static typename EnableIf<
HasDecorator<ds, MO_ACQUIRE>::value, T>::type
load_internal(void* addr);
template <DecoratorSet ds, typename T>
static typename EnableIf<
HasDecorator<ds, MO_RELAXED>::value, T>::type
load_internal(void* addr);
template <DecoratorSet ds, typename T>
static inline typename EnableIf<
HasDecorator<ds, MO_UNORDERED>::value, T>::type
load_internal(void* addr) {
return *reinterpret_cast<T*>(addr);
}
load 继承 RawAccessBarrier 的 DecoratorSet decorators,并自己持有返回值类型 T。并且派发到四个 load_internal 之一。由于在静态已经 verify 过,内存序装饰器类别中有且只能有一个装饰器被设置,所以一定是可以唯一静态派发到其中一个 load_internal 的,即分别是 MO_SEQCST,MO_ACQUIRE,MO_RELAXED 和 MO_UNORDERED 语义的 load 操作上(load一般没有 release 语义,所以如果是 release load 的话 Failure 就会模板匹配失败成为 error,正好是符合预期的)。
RawAccessBarrier oop operation
RawAccessBarrier 对 OOP 的操作同时要考虑 OOP 指针压缩的问题,以及原子操作内存序的问题。将这二者结合,就成为了 RawAccessBarrier 中有关 oop 的一系列操作,它们是 RawAccessBarrier 类对外主要暴露的接口。
template <typename T>
static void oop_store(void* addr, T value);
template <typename T>
static void oop_store_at(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset, T value);
template <typename T>
static T oop_load(void* addr);
template <typename T>
static T oop_load_at(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset);
template <typename T>
static T oop_atomic_cmpxchg(void* addr, T compare_value, T new_value);
template <typename T>
static T oop_atomic_cmpxchg_at(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset, T compare_value, T new_value);
template <typename T>
static T oop_atomic_xchg(void* addr, T new_value);
template <typename T>
static T oop_atomic_xchg_at(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset, T new_value);
template <typename T>
static bool oop_arraycopy(arrayOop src_obj, size_t src_offset_in_bytes, T* src_raw,
arrayOop dst_obj, size_t dst_offset_in_bytes, T* dst_raw,
size_t length);
static void clone(oop src, oop dst, size_t size);
以 oop_load 为例子。
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
template <typename T>
inline T RawAccessBarrier<decorators>::oop_load(void* addr) {
typedef typename AccessInternal::EncodedType<decorators, T>::type Encoded;
Encoded encoded = load<Encoded>(reinterpret_cast<Encoded*>(addr));
return decode<T>(encoded);
}
首先通过 EncodedType 推导出本次 OOP access 的 OOP 类型是怎样的,即确定是 narrowOop 还是 oop。然后通过 load 操作从地址 addr 中原子地将这个 oop 指针(或者 32bit narrowOop 指针)拿出来,最后通过 decode 调用 CompressedOops 解码(如果 Encoded 是 oop 那么原样返回,如果是 narrowOop 那么经过一些计算得到 oop),最终返回出 T 这个类型(实际上就应该是 oop 类型)。
Step 4: Runtime dispatch
进入流水线这一步的,应该就是 非 Raw Access 且是 OOP Access 的。由于运行时分发需要在 JVM 实际跑起来之后才能知道使用的是什么 GC,以及别的一些运行时信息,所以需要附加的 barrier 在静态是不确定的,所以最开始这个 barrier pointer 会指向一个初始化函数(accessor resolution funciton),在首次调用时会解析到具体的函数并存储,在之后就直接访问它就行了,有点类似于动态链接库里面用于延迟绑定的 GOT / PLT。
先看 Access Functions 的定义。
AccessFunctionTypes
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
struct AccessFunctionTypes {
typedef T (*load_at_func_t)(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset);
typedef void (*store_at_func_t)(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset, T value);
typedef T (*atomic_cmpxchg_at_func_t)(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset, T compare_value, T new_value);
typedef T (*atomic_xchg_at_func_t)(oop base, ptrdiff_t offset, T new_value);
typedef T (*load_func_t)(void* addr);
typedef void (*store_func_t)(void* addr, T value);
typedef T (*atomic_cmpxchg_func_t)(void* addr, T compare_value, T new_value);
typedef T (*atomic_xchg_func_t)(void* addr, T new_value);
typedef bool (*arraycopy_func_t)(arrayOop src_obj, size_t src_offset_in_bytes, T* src_raw,
arrayOop dst_obj, size_t dst_offset_in_bytes, T* dst_raw,
size_t length);
typedef void (*clone_func_t)(oop src, oop dst, size_t size);
};
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
struct AccessFunctionTypes<decorators, void> {
typedef bool (*arraycopy_func_t)(arrayOop src_obj, size_t src_offset_in_bytes, void* src,
arrayOop dst_obj, size_t dst_offset_in_bytes, void* dst,
size_t length);
};
template <DecoratorSet decorators>
struct AccessFunctionTypes<decorators, void> {
typedef bool (*arraycopy_func_t)(arrayOop src_obj, size_t src_offset_in_bytes, void* src,
arrayOop dst_obj, size_t dst_offset_in_bytes, void* dst,
size_t length);
};
这个类定义了各个 OOP operation 对应的函数类型。其中类的元参数中 DecoratorSet decorators 是本次访问的装饰器集合,typename T 是 OOP operation 的返回类型。
AccessFunction
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T, BarrierType barrier> struct AccessFunction {};
#define ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(bt, func) \
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T> \
struct AccessFunction<decorators, T, bt>: AllStatic{ \
typedef typename AccessFunctionTypes<decorators, T>::func type; \
}
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_STORE, store_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_STORE_AT, store_at_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_LOAD, load_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_LOAD_AT, load_at_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_ATOMIC_CMPXCHG, atomic_cmpxchg_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_ATOMIC_CMPXCHG_AT, atomic_cmpxchg_at_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_ATOMIC_XCHG, atomic_xchg_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_ATOMIC_XCHG_AT, atomic_xchg_at_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_ARRAYCOPY, arraycopy_func_t);
ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION(BARRIER_CLONE, clone_func_t);
#undef ACCESS_GENERATE_ACCESS_FUNCTION
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T, BarrierType barrier_type>
typename AccessFunction<decorators, T, barrier_type>::type resolve_barrier();
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T, BarrierType barrier_type>
typename AccessFunction<decorators, T, barrier_type>::type resolve_oop_barrier();
针对每一个 OOP operation 的函数类型,都声明一个 template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T> struct AccessFunction<decorators, T, bt>。这个 AccessFunction 作为元函数主要是返回里存储的 typename AccessFunctionTypes<decorators, T>::func type, 即根据 barrier type 就能推导对应哪一个 access function type(OOP operatio 的函数签名)。
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T, BarrierType barrier_type>
typename AccessFunction<decorators, T, barrier_type>::type resolve_barrier();
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T, BarrierType barrier_type>
typename AccessFunction<decorators, T, barrier_type>::type resolve_oop_barrier();
所以这两个函数 resolve_barrier 和 resolve_oop_barrier 都是这样的,根据传入的装饰器集合、访问的值类型 T 以及对应屏障类型,解析出来应该使用的访问函数的函数签名(函数类型)是怎样的。
AccessLocker
class AccessLocker {
public:
AccessLocker();
~AccessLocker();
};
bool wide_atomic_needs_locking();
为位宽较大的类型模拟原子操作。
load 举例说明
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T, BarrierType type>
struct RuntimeDispatch: AllStatic {};
Runtime dispatch 有一个通用的 RuntimeDispatch 类,但是针对每一种 OOP operation 都会各自偏特化一个 RuntimeDispatch 出来,比如 load 的就是:
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
struct RuntimeDispatch<decorators, T, BARRIER_LOAD>: AllStatic {
typedef typename AccessFunction<decorators, T, BARRIER_LOAD>::type func_t;
static func_t _load_func;
static T load_init(void* addr);
static inline T load(void* addr) {
assert_access_thread_state();
return _load_func(addr);
}
};
只有设置了 BARRIER_LOAD 的才会偏特化到这个定义上面,即对应 load 操作。在调用 load 时,会委派给 _load_func 即类里面存储的 static func_t _load_func,这个 func_t 函数类型是静态就能够确定好的,就是 typedef T (*load_func_t)(void* addr);。这个 _load_func 在初始状态下是这样的:
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
typename AccessFunction<decorators, T, BARRIER_LOAD>::type
RuntimeDispatch<decorators, T, BARRIER_LOAD>::_load_func = &load_init;
即指向了本类中定义的 load_init 函数。这个函数,以及别的 OOP operation 对应的 store_init,atomic_cmpxchg_init 等等初始化函数的签名都是没有实际意义的,仅仅是为了和各自的 func_t 保持一致以便静态存储在 _load_func 等里面。它们在内部做的事情都是一样的,以 load_init 为例:
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename T>
T RuntimeDispatch<decorators, T, BARRIER_LOAD>::load_init(void* addr) {
func_t function = BarrierResolver<decorators, func_t, BARRIER_LOAD>::resolve_barrier();
_load_func = function;
return function(addr);
}
它会调用 BarrierResolver 的函数根据运行时信息来解析出具体是哪一个实际的 OOP operation 函数要使用,并且存储到 _load_func 中,并在初次调用中直接调用一次;后续调用就会直接走 function 了,BarrierResolver::resolve_barrier 对每一种 OOP operation 只会执行一次。
Step 5.a Barrier resolution
// Resolving accessors with barriers from the barrier set happens in two steps.
// 1. Expand paths with runtime-decorators, e.g. is UseCompressedOops on or off.
// 2. Expand paths for each BarrierSet available in the system.
template <DecoratorSet decorators, typename FunctionPointerT, BarrierType barrier_type>
struct BarrierResolver: public AllStatic
根据注释可以知道,Barrier resolution 分两步走。
- 展开装饰器(取决于是否采用了 UseCompressedOops)。
- 根据 GC 算法选择。
Expand decorator set
static FunctionPointerT resolve_barrier_rt() {
if (UseCompressedOops) {
const DecoratorSet expanded_decorators = decorators | INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS;
return resolve_barrier_gc<expanded_decorators>();
} else {
return resolve_barrier_gc<decorators>();
}
}
static FunctionPointerT resolve_barrier() {
return resolve_barrier_rt();
}
在 Step 4 末尾介绍的调用 resolve_barrier 实际上会直接调用 resolve_barrier_rt。在这里首先根据是否启用了 UseCompressedOops 将装饰器集合添加 INTERNAL_RT_USE_COMPRESSED_OOPS。并且调用 resolve_barrier_gc。
resolve_barrier_gc 根据 HasDecorator<ds, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP> 进行 SFINAE,即根据是否是 OOP 访问派发到不同的函数上。
对于 INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP 的:
template <DecoratorSet ds>
static typename EnableIf<
HasDecorator<ds, INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP>::value,
FunctionPointerT>::type
resolve_barrier_gc() {
BarrierSet* bs = BarrierSet::barrier_set();
assert(bs != nullptr, "GC barriers invoked before BarrierSet is set");
switch (bs->kind()) {
#define BARRIER_SET_RESOLVE_BARRIER_CLOSURE(bs_name) \
case BarrierSet::bs_name: { \
return PostRuntimeDispatch<typename BarrierSet::GetType<BarrierSet::bs_name>::type:: \
AccessBarrier<ds>, barrier_type, ds>::oop_access_barrier; \
} \
break;
FOR_EACH_CONCRETE_BARRIER_SET_DO(BARRIER_SET_RESOLVE_BARRIER_CLOSURE)
#undef BARRIER_SET_RESOLVE_BARRIER_CLOSURE
default:
fatal("BarrierSet AccessBarrier resolving not implemented");
return nullptr;
};
}
从 BarrierSet 中根据对应 GC 算法取出合适的 GC 屏障集。并且对应 GC 算法进入 Post-runtime dispatch 返回真正的 OOP operation 函数。
而对于不是 INTERNAL_VALUE_IS_OOP 的,仅仅是将 oop_access_barrier 换成 access_barrier,其他地方没有区别。
然后现在先来看一下这堆宏是什么。完整的 context 如下。
// Do something for each concrete barrier set part of the build.
#define FOR_EACH_CONCRETE_BARRIER_SET_DO(f) \
f(CardTableBarrierSet) \
EPSILONGC_ONLY(f(EpsilonBarrierSet)) \
G1GC_ONLY(f(G1BarrierSet)) \
SHENANDOAHGC_ONLY(f(ShenandoahBarrierSet)) \
ZGC_ONLY(f(XBarrierSet)) \
ZGC_ONLY(f(ZBarrierSet))
#define BARRIER_SET_RESOLVE_BARRIER_CLOSURE(bs_name) \
case BarrierSet::bs_name: { \
return PostRuntimeDispatch<typename BarrierSet::GetType<BarrierSet::bs_name>::type:: \
AccessBarrier<ds>, barrier_type, ds>::oop_access_barrier; \
} \
break;
FOR_EACH_CONCRETE_BARRIER_SET_DO(BARRIER_SET_RESOLVE_BARRIER_CLOSURE)
#undef BARRIER_SET_RESOLVE_BARRIER_CLOSURE
很显然使用了 X-macro 技巧。诸如 G1GC_ONLY 这种是编译开关,是在构建JDK 的时候指定的。而对于打开编译开关的 GC 算法,比如我们打开了 G1GC_ONLY 在构建这个 JDK 时包括了 G1 GC 算法,那么这段宏就会将 G1BarrierSet 作为 bs_name 宏参数传递给 BARRIER_SET_RESOLVE_BARRIER_CLOSURE。那么宏展开为:
case BarrierSet::G1BarrierSet: {
return PostRuntimeDispatch<typename BarrierSet::GetType<BarrierSet::G1BarrierSet>::type::
AccessBarrier<ds>, barrier_type, ds>::oop_access_barrier;
}
break;
整段就是生成一堆 switch 语句而已。会根据拿到的 BarrierSet 类型做 Fake RTTI,然后做 Post-runtime dispatch。
Step 5.b Post-runtime dispatch
在最终调用 BarrierSet::AccessBarrier 前还是要过一层这个 PostRuntimeDispatch 的。看注释更清楚:
// Step 5.b: Post-runtime dispatch.
// This class is the last step before calling the BarrierSet::AccessBarrier.
// Here we make sure to figure out types that were not known prior to the
// runtime dispatch, such as whether an oop on the heap is oop or narrowOop.
// We also split orthogonal barriers such as handling primitives vs oops
// and on-heap vs off-heap into different calls to the barrier set.
template <class GCBarrierType, BarrierType type, DecoratorSet decorators>
struct PostRuntimeDispatch: public AllStatic { };
这一步会在运行时弄清楚在静态不清楚的信息,比如说之前提到的 P 类型是 HeapWord* 的时候到底加载的对象指针是 oop 还是 narrowOop。以及会使用到 ON_ 开头的那些访问位置装饰器。
PostRuntimeDispatch 这个类的定义方式和 RuntimeDispatch 很像,都是有一个空实现的模板类,然后根据每一种 OOP operation 偏特化出一个类。
还是以 load 操作举例。
template <class GCBarrierType, DecoratorSet decorators>
struct PostRuntimeDispatch<GCBarrierType, BARRIER_LOAD, decorators>: public AllStatic {
template <typename T>
static T access_barrier(void* addr) {
return GCBarrierType::load_in_heap(reinterpret_cast<T*>(addr));
}
static oop oop_access_barrier(void* addr) {
typedef typename HeapOopType<decorators>::type OopType;
if (HasDecorator<decorators, IN_HEAP>::value) {
return GCBarrierType::oop_load_in_heap(reinterpret_cast<OopType*>(addr));
} else {
return GCBarrierType::oop_load_not_in_heap(reinterpret_cast<OopType*>(addr));
}
}
};
很明显,对于基本类型,access_barrier 会调用 GCBarrierType::load_in_heap 去实现。对于 OOP 的访问,根据访问位置的不同,oop_access_barrier 会调用 GCBarrierType::oop_load_in_heap 或者是 GCBarrierType::oop_load_not_in_heap。
这样,Post-runtime dispatch 对于非 Raw Access 的访问,又根据基本类型访问、Java 堆上 OOP 访问以及 Java 堆外 OOP 访问分别派发了三种 access barrier。
GC Barrier
How does Narrow OOP structure look like
在 64 bit 平台上一个 oop 指针占用 8 bytes 的大小,在 Java 堆中各种地方都塞满了 OOP 指针,如果大家都是 8 bytes 那占用的大小就比较大。所以 64 bit 平台上 JVM 使用了压缩指针技术 Compressed OOP。它引入了一种窄指针 narrowOop,能够在堆大小满足一定要求时采用 32 bits (4 bytes) 表示一个 oop 指针。
有多种 Narrow OOP encoding mode。
0 - no encoding
在 NarrowOopHeapBaseMin + 堆大小 < 4GB 时,指针天然可以用 32 bits 表示,此时不需要任何编码,直接将 oop 强转为 uint32_t 表示即可。但这意味着原本 64 bits 上高 16 bits 的空闲空间是不存在的,因为都截断了。
1 - zero based compressed oops
在 NarrowOopHeapBaseMin + 堆大小 < 32GB,采用这种压缩方式。
// ObjectAlignmentInBytes = 8 by default
// So LogMinObjAlignmentInBytes = 3 by default
LogMinObjAlignmentInBytes = exact_log2(ObjectAlignmentInBytes);
// Maximal size of heap where unscaled compression can be used. Also upper bound
// for heap placement: 4GB.
const uint64_t UnscaledOopHeapMax = (uint64_t(max_juint) + 1);
if ((uint64_t)heap_space.end() > UnscaledOopHeapMax) {
// Didn't reserve heap below 4Gb. Must shift.
set_shift(LogMinObjAlignmentInBytes);
}
set_shift 为 3,即当 NarrowOopHeapBaseMin + 堆大小 超过了 4GB,那么利用对象是 8 Bytes 对齐的特性就很重要,这可以省下 3 bits 的空间。
if ((uint64_t)heap_space.end() <= OopEncodingHeapMax) {
// Did reserve heap below 32Gb. Can use base == 0;
set_base(0);
} else {
set_base((address)heap_space.compressed_oop_base());
}
如果 NarrowOopHeapBaseMin + 堆大小 没超过 32GB 那么 base 就是 0,否则就需要有一个 heap base 作减法以保证结果能放到 32 bits 中。
2/3 - heap based compressed oops
如上,超过 32GB 就需要减。
Algorithm
inline narrowOop CompressedOops::encode_not_null(oop v) {
assert(!is_null(v), "oop value can never be zero");
assert(is_object_aligned(v), "address not aligned: " PTR_FORMAT, p2i(v));
assert(is_in(v), "address not in heap range: " PTR_FORMAT, p2i(v));
uint64_t pd = (uint64_t)(pointer_delta((void*)v, (void*)base(), 1));
assert(OopEncodingHeapMax > pd, "change encoding max if new encoding");
narrowOop result = narrow_oop_cast(pd >> shift());
assert(decode_raw(result) == v, "reversibility");
return result;
}
(pointer - base) >> shift。所以只要 OOP 指针可能的取值上下限不超过 32GB,那么就可以放到一个 narrowOop 中。
Introduction
Miscellaneous content.
Newbee
NOTE: THIS SECTION IS COMPOSED OF NON-ORIGINAL CONTENT
注意:本节由非原创性内容组成
This section contains a lot of non-original content collection. But… why this section is called “Newbee”? If you are asking this question, then you are not a Chinese I guess. 收集点牛逼或者有意思的内容,非原创合集。
小红书上HR发约会贴实际上在查竞业 Bytedance HR Non-compete clause (NCC) checking using dating post on Rednote
- Collection date: 20251027
- Tags: #Rednote #NCC #小红书 #竞业 #HR
- 有人在 xhs 上发帖子,内容是约会 dating 求帮忙查男生成分,但实际上有可能是查这个人的竞业情况。
RISC-V KVM Forum 2025
- Collection date: 20251028
- Tags: #KVM #RISC-V #Linux #Virtualization #vGPU
- It’s here: https://kvm-forum.qemu.org/2025/.
自建IP使用Claude
自建节点,IP干净了就好了。教程油管搜一下有很多,推荐参考网站digvps。